Businesses and individuals are constantly seeking ways to elevate their online presence and maximize their websites’ performance. One technology that has revolutionized the way websites are hosted and managed is cloud hosting. With its remarkable scalability, flexibility, and reliability, cloud hosting has become the go-to solution for those who aspire to soar above the rest in the virtual realm.

According to recent statistics, 31% of organizations predict that by the end of 2023, more than 75% of their workloads will run in the cloud.
These numbers reflect the growing recognition of cloud hosting as a game-changer in the digital landscape.
But what exactly is cloud hosting? How does it differ from traditional hosting methods? In this article, we will unravel the mysteries of cloud hosting and shed light on its unique features that make it a game-changer in the world of web hosting.
- Cloud hosting utilizes virtualization and resource pooling for flexible and scalable hosting services
- Cloud hosting offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, allowing businesses to pay for needed resources and scale up or down
- Reputable cloud hosting providers prioritize security, implementing robust measures, encryption, and compliance standards to protect data
- The pay-as-you-go pricing model enables cost optimization and efficient resource allocation
- Load balancing is vital in distributing network traffic across multiple servers, optimizing performance, and resource utilization
What Is Cloud Hosting?

Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting that uses a network of servers to store and deliver website content.
This means your website is not stored on a single server but on a network of servers spread across multiple locations.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Hosting?
Cloud Hosting provides several benefits, including:
- Flexible pricing structure – You only pay for what you use
- Easy to scale server resources – You can quickly scale up or down your resources as needed
- Redundant server environment – If one server fails, another can take its place, ensuring high uptime and availability
- High uptime and availability – Cloud hosting takes advantage of many servers spread across the cloud network, providing great reliability and uptime
- Faster website speed and performance – Servers are in different regions, so content is delivered to users faster
Learn more about the Benefits of Cloud Hosting Solutions
How Does Cloud Hosting Work?
Cloud hosting works by combining cloud servers and virtual private servers to offer scalable computing resources and enhanced hosting efficiency. It involves the following key components:
Virtualization
Virtualization is the process of creating multiple virtual machines (VMs) from a single physical server. It enables the creation of multiple virtual servers by abstracting the server’s physical resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage. This allows multiple websites to share the same physical resources, utilizing cloud servers and computing resources efficiently.
Here’s how it works:
- A hypervisor is installed on the physical server. The hypervisor is a software program that creates and manages the virtual servers.
- The hypervisor divides the physical resources of the server into virtual resources. Each virtual resource is assigned to a virtual server.
- The virtual servers are then created. Each virtual server has its operating system and applications.
Resource Pooling
Resource pooling involves consolidating various resources, including processing power, memory, storage, and bandwidth, into a shared pool that can be dynamically allocated and distributed among different applications and users based on their specific needs.
This means you don’t have to purchase or maintain dedicated hardware, as the servers provide scalable computing resources. You only pay for the resources that you use.
Resource pooling is implemented in three ways:
- Hardware virtualization – The process of dividing a physical server into multiple virtual machines (VMs)
- Software virtualization – Using a software layer to abstract the physical resources of a server
- Cloud computing – This involves using a network of remote servers to store and deliver data and applications
Distributed Architecture
Distributed architecture is the distribution of virtual servers across multiple physical machines and data centers.
In a distributed architecture, each virtual server is hosted on a different physical machine. This means that if one physical machine fails, the virtual server running on it will not be affected. The virtual server will be automatically moved to another physical machine.
By distributing virtual servers across multiple data centers, cloud providers can ensure that your website or application is always available, even if one data center fails.
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource utilization and improve performance. There are two main types of load balancing:
- Hardware load balancers – These are physical devices between the internet and your servers. They distribute traffic across your servers based on various factors, such as server capacity, location, and health.
- Software load balancers – These are software applications that run on your servers. They distribute traffic across your servers similarly to hardware load balancers.
Load balancers work by inspecting incoming network traffic and routing it to the appropriate server. They also perform a variety of other tasks, such as Health checking, SSL offloading, and Web application firewall (WAF).
Scalability
Scalability is the ability to easily increase or decrease the resources allocated to a website or application. This is done quickly and easily, without any downtime.
Cloud hosting, working through cloud servers, is highly scalable because it uses a pay-as-you-go model, allowing for efficient management of computing resources. This means that you only pay for the resources that you use. As your website or application grows, you can easily add more resources to meet the demand.
Cloud hosting excels in horizontal scalability, which involves scaling resources by adding more instances or replicas rather than increasing the capacity of individual servers.
Pay-As-You-Go Model
The pay-as-you-go model is a pricing model where you only pay for the resources that you use. This means you don’t have to commit to a long-term contract or pay for resources you’re not using.
To optimize your costs using the pay-as-you-go model:
- Use spot instances – Spot instances are unused cloud resources available at a discounted price. You can use spot instances to save money on your cloud hosting costs.
- Use reserved instances – Reserved instances are cloud resources you can reserve for a time. By reserving instances, you can get a discount on your cloud hosting costs.
- Use auto-scaling – Auto scaling is a feature that allows you to automatically scale your cloud resources up or down based on demand. This can help you save money by only using the needed resources.
The pay-as-you-go model is a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
Security
The Statista Research Department states, “In 2021, 64% of respondents named data loss or leakage as their biggest cloud security concern.â€
To mitigate this, cloud providers offer a variety of cloud server security features to help protect your data, including:
- Physical security – Cloud providers’ data centers are located in secure facilities. Access control, round-the-clock monitoring, and perimeter security are in place to protect these facilities.
- Network security – The providers use security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption to protect your data in transit and at rest
- Application security – Cloud providers will check and advise on fixing your apps for security flaws. They also offer a variety of security features to help protect your applications, such as authentication, authorization, and access control.
- Data backup and recovery – Most providers offer a variety of data backup and recovery options
Cloud providers also implement something called data redundancy. This security measure safeguards against data loss in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
Cloud providers use a variety of techniques to achieve data redundancy, including:
- Replication – Data is replicated across multiple servers. This means your data is stored on multiple servers, so if one server fails, your data is still available on the other servers.
- Fault tolerance – Fault-tolerant systems have multiple components that can fail without affecting the availability of your data
Which Cloud Hosting Providers Are Popular in the Market?

With the increasing popularity and demand for cloud hosting, several providers have emerged as leaders in the market. While the landscape is dynamic and subject to change, some of the popular cloud hosting companies that have gained widespread recognition and trust include:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the leading cloud computing platform, with over 300 services used by millions of customers worldwide.
In the first quarter of 2023, Synergy Research Group estimated that Amazon held a market share of 32% in the worldwide cloud infrastructure market.
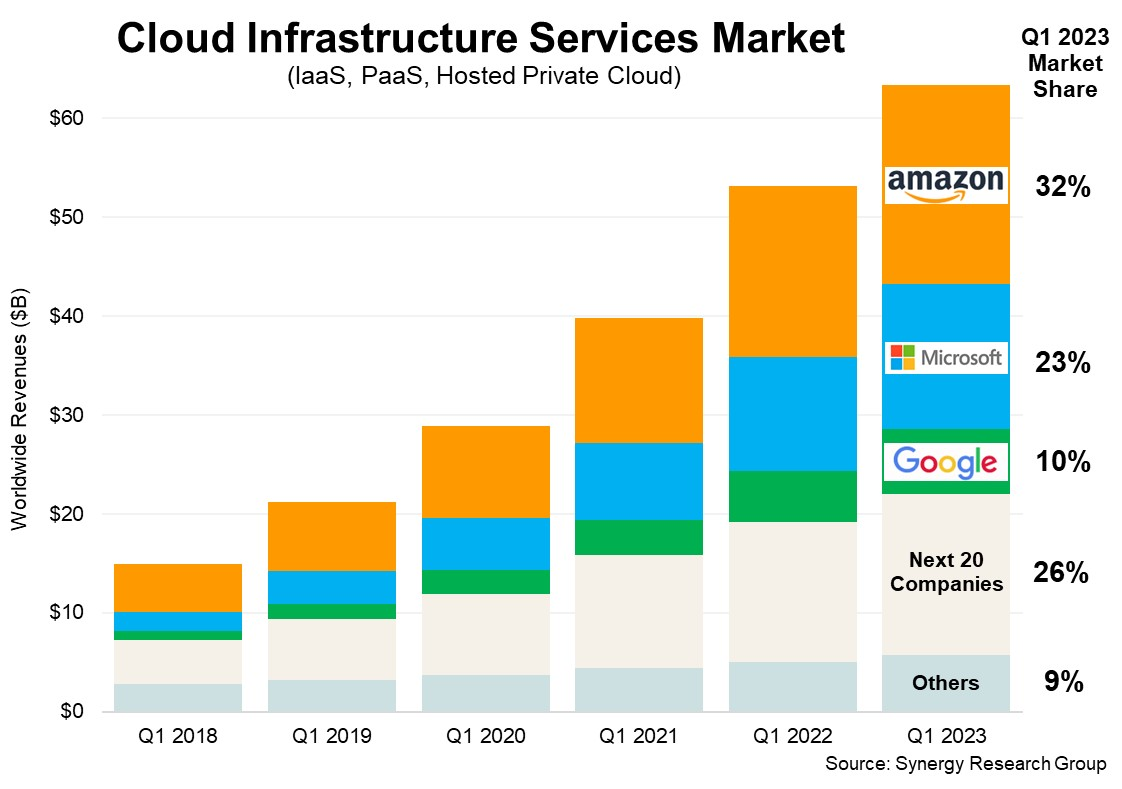
Some of the key features and services offered by AWS include:
- Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) – EC2 is a service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It allows you to launch and run virtual machines (VMs) on demand.
- Simple Storage Service (S3) – S3 provides object storage in the cloud. It allows for storing any data, including images, videos, documents, and applications.
- Relational Database Service (RDS) – RDS provides managed relational databases in the cloud. It allows you to run popular relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure.
AWS also offers many other services, such as computing, networking, analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services that runs on the same infrastructure that Google uses for its end-user products, such as Google Search and YouTube.
Alongside a set of management tools, it provides a series of modular cloud services, including computing, data storage, data analytics, and machine learning. GCP is a good choice to scale your IT infrastructure quickly and easily.
GCP offers a broad range of services, like:
- Compute Engine – Compute Engine provides virtual machines (VMs) in the cloud
- App Engine – A platform for developing and hosting web applications in Google-managed data centers
- BigQuery – BigQuery provides a fully managed, petabyte-scale analytics data warehouse
- Cloud SQL – As the name states, Cloud SQL service, provides fully managed relational databases in the cloud
Microsoft Azure
The 2023 State of the Cloud Report states that Azure has slightly surpassed AWS in enterprise adoption, with 80% of enterprises utilizing Azure compared to 77% for AWS. Microsoft Azure is popular among enterprises because it integrates with other Microsoft products, such as Office 365 and Microsoft Teams.
Here are some of the key features and services of Microsoft Azure:
- Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) – Azure VMs provide resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It allows you to launch and run virtual machines (VMs) on demand.
- Azure Blob Storage – An object storage service for unstructured data, such as text or binary data
- Azure Functions – Azure Functions lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. It is a serverless computing platform that allows you to focus on writing code and not worry about the underlying infrastructure.
Other Notable Providers
In addition to the prominent cloud hosting companies mentioned earlier, several other notable players in the market offer reliable and feature-rich cloud hosting solutions. Here are a few:
- IBM Cloud – IBM Cloud suite runs on the same infrastructure that IBM uses for its end-user products, such as IBM Watson and IBM Cloud Pak for Data. It emphasizes enterprise-grade security, compliance, and hybrid cloud capabilities, making it attractive for businesses with complex requirements. IBM Cloud also provides AI-powered services, blockchain solutions, and data analytics tools to support innovation and digital transformation.
- Oracle Cloud – Oracle Cloud provides comprehensive solutions for enterprise workloads, with strong integration with Oracle’s database and application technologies. It offers advanced capabilities in autonomous databases, AI-driven analytics, and high-performance computing.
- Alibaba Cloud – Alibaba Cloud is a leading cloud hosting provider in China and has rapidly expanded its global presence. Alibaba Cloud’s strength lies in its robust infrastructure, scalability, and extensive services tailored to the Asian market.
What Factors Should You Consider When Selecting a Cloud Hosting Provider?
When selecting a cloud hosting provider, consider these factors to ensure the choice aligns with your needs and requirements.
Performance and Scalability
Performance refers to how easily and quickly users can access your website or application.
Scalability refers to the ability of your website or application to handle increased traffic without affecting performance.
When choosing a cloud hosting provider, assess their performance capabilities. This includes factors such as:
- Server uptime: The percentage of time a server is available to users. High uptime is important if your business needs its websites or applications to be available 24/7.
- Network speed: The speed at which data can be transferred between your website or application and the user’s device
- Traffic Handling: The capability of the hosting provider to manage high-traffic loads efficiently, ensuring that your website or application performs reliably during peak usage periods.
Pricing and Cost Structure
Look for flexible pricing models and the availability of different instance types to accommodate changing demands. There are several different pricing models that many cloud hosting providers offer:
- Pay-as-you-go – Pay-as-you-go pricing is a cost-effective option for businesses that only need cloud hosting for a short period. Under this model, you only pay for the resources you use.
- Subscription-based – Subscription-based pricing is a good option for businesses that need cloud hosting for a longer period. This model offers a monthly or yearly subscription with a set amount of resources.
- Bundled packages – Bundled packages offer a variety of resources, such as storage, bandwidth, and computing power, at a discounted price. This is a good option for businesses that need a lot of resources.
To know which is the best pricing model for your business, ask yourself these questions:
- How much traffic does my website or application receive?
- How much storage do I need?
- How much bandwidth do I need?
- What features do I need?
- What is my budget?
Support and Service Level Agreements
There will be times when you need help with your website or application. How responsive and reliable will the provider be? Look for guarantees or service level agreements (SLAs) that ensure a high level of availability and minimal downtime.
SLAs typically include guarantees for uptime and availability and remedies for service disruptions. When selecting a cloud hosting provider, review their SLAs to ensure they meet your requirements.
For example, a 99.9% uptime SLA means that the provider promises that your website or application will be available 99.9% of the time.
Security and Compliance
The 2022 State of Cloud Security Report reported that 80% of firms surveyed experienced at least one cloud security breach in 2022.
The provider should ensure your data is encrypted at rest and in transit. This means it should be scrambled so unauthorized individuals cannot read it. Further, depending on your industry, ensure that the cloud hosting provider adheres to relevant compliance regulations.
Examples include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for handling European Union citizen data
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare data
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for handling payment card information
Case Studies or Real-World Examples
Case studies and real-world examples help you understand how the provider has helped other businesses and organizations achieve their goals. This way, you can know the provider’s strengths and weaknesses.
Case studies offer evidence of the provider’s performance in real-world scenarios. They provide insights into how the provider’s infrastructure and services perform under different workloads, traffic spikes, or scalability demands.
Reviewing these case studies allows you to evaluate the provider’s track record and assess if their performance aligns with your expectations.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting has gained significant popularity in recent years, but some common misconceptions exist. Let’s address a few of these misconceptions:
Myth 1: Cloud Hosting Is Too Expensive
Cloud hosting can be more expensive than traditional hosting solutions in certain cases. However, it’s more cost-effective, especially for businesses that need a lot of flexibility and scalability.
Unlike traditional hosting, where businesses may need to invest in costly hardware and infrastructure upfront, cloud hosting operates on a pay-as-you-go model. This allows you to only pay for the resources you use, saving you money if you don’t need a lot of resources.
Check out our recommended list of Cheap Cloud Hosting ProvidersMyth 2: Cloud Hosting Is Not Secure
Web hosting providers invest heavily in cloud security measures to protect their customers’ data.
Reputable web hosting providers implement advanced security measures, including data encryption, network firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regular security audits.
In addition, providers have multiple data centers located around the world. This helps to protect data from physical disasters.
Myth 3: Cloud Hosting Is Difficult to Manage
Cloud hosting services offer intuitive web-based interfaces and management consoles that allow you to easily manage your cloud resources.
These interfaces provide a centralized view of the infrastructure, enabling you to provision, monitor, and configure resources with just a few clicks.
Conclusion
So, what is cloud hosting? Simply put, it is a powerful solution that offers businesses numerous benefits, including scalability, cost-efficiency, and enhanced security.
As you embark on your cloud hosting journey, remember to assess your specific requirements, seek reliable customer support, and ensure the provider aligns with industry compliance standards. Utilize the resources and information available to make an informed decision that suits your business goals and objectives.
Remember, a well-chosen cloud hosting provider can be a solid foundation for your online endeavors.
Next Steps: What Now?
- Evaluate your business needs, including anticipated traffic, storage requirements, and scalability needs.
- Check out our recommended list of the Best Cloud Hosting Providers
- Research and compare the Cost of Cloud Hosting
- Explore customer reviews and testimonials
- Test Cloud Hosting plans by taking advantage of Free Cloud Hosting trial offers
Learn More About Cloud Hosting
- Benefits of Cloud Hosting
- Guide to Cloud Hosting
- What Are Cloud Servers?
- What Is Cloud VPS?
- What Is Managed Cloud Hosting?
- What Is Private Cloud Hosting?
- What Is Hybrid Cloud?
- Cloud Server Security
- Types of Cloud Computing
- Types of Virtualization in Cloud Computing for Businesses
- Types of Cloud Deployment Models
- Data Centers in Cloud Computing
- Public Private Hybrid Cloud
- Cloud Computing in Small Business
- Cloud Computing Advantages and Disadvantages
- Colocation Cloud: Smart Choice for Your Company’s Data Center Needs
- Dedicated Vs. Cloud Hosting: Which Is Right For You?









