
We applied the blog SEO tips in this guide to achieve a staggering 575% growth in organic traffic on the Hostadvice blog in just one year.
The blog traffic grew from 3.45K in November 2022 to 23.3K clicks in November 2023.
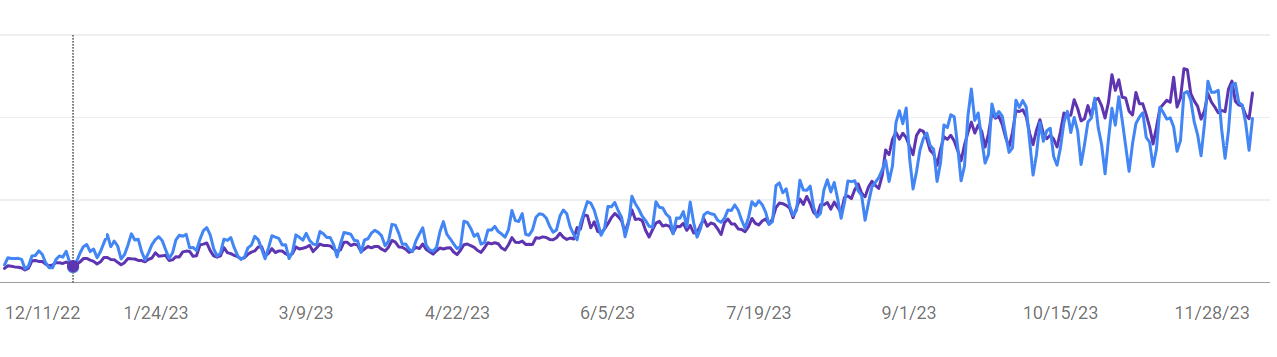
Let’s begin by understanding the basics before we move on to the specific tips and strategies.
What Is Blog SEO?
Blog SEO refers to the set of strategies and techniques used to improve the visibility and ranking of blog content in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The goal of blog SEO is to attract more organic (non-paid) traffic to a blog by making the content more discoverable and appealing to search engines like Google.
This practice includes crafting quality content, on-page optimization, and building backlinks to attract organic traffic and reader engagement.
Why Is Blog SEO Important?
Starting a blog is easy, but making it stand out and climbing search engine rankings requires SEO.
Successful blog SEO can lead to the following benefits:
- Increased Authority
- Better search engine visibility
- Increased organic website traffic
- Improved user experience
- Targeting of interested audiences
- Access to valuable data and insights
In Fact, a survey by Orbit Media shows that 66% of bloggers use SEO to promote their content.
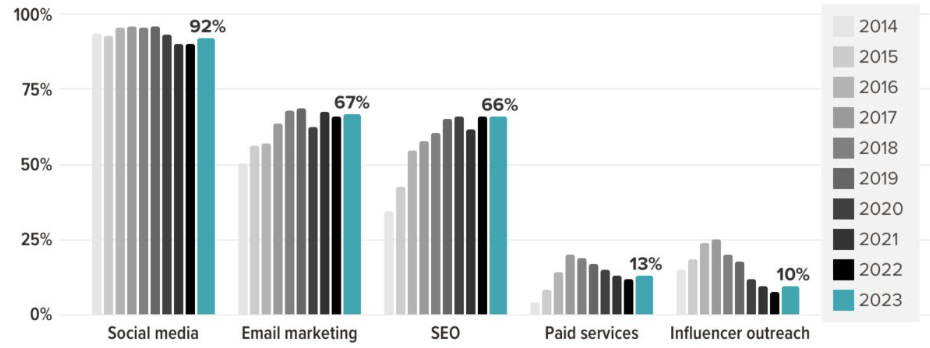
Source: Orbit Media
Does Better Blog SEO Affect Your Website’s Overall Ranking?
When your blog content ranks higher and attracts more traffic, it signals to search engines that your website provides valuable and relevant content. This improves user engagement, and enhances the authority of your website.
As a result, the overall ranking of your website is improved.
Additionally, high-quality blog content can encourage visitors to spend more time on your site, explore other pages, and reduce bounce rates. These factors are considered by search engines when determining website rankings.
Now that we’ve covered the essentials let’s delve into these actionable blog SEO tips.
Blog SEO Tips & Best Practices
To learn how to optimize your blog for SEO (search engine optimization), check out our tested tips. Implementing these tips led to a 575% growth in our blog’s organic traffic.
1. Identify Target Keywords for Every Post
The main goal of this step is to find one main keyword for each blog post and a few secondary keywords.
The right keywords enable you to reach the desired audience and resonate with their search intent.
Let’s explore the systematic approach and tools you need to master this crucial aspect of blog optimization.
Research the topic
Read existing content to gather information and understand what’s already out there. This can include articles, blogs, forums, and books. Pay attention to recurring themes, questions, and discussions.
For example, if your topic is “home workout,†look for articles in fitness magazines or websites like Men’s Health, Women’s Health, or Healthline that specifically discuss home workouts.
You can also check out fitness forums such as Bodybuilding.com’s forum or Reddit’s r/Fitness and r/homefitness.
These platforms are rich with actual user experiences, discussions about different workout strategies, and advice on home workout equipment.
Identify Your Audience’s Needs
Consider what your target audience might be looking for about your topic.
- What problems do they have?
- What solutions might they be searching for?
For instance, if your topic is about ‘home workouts,’ consider whether your audience is beginners, looking for quick workouts, or specific types of exercises.
Use Keyword Research Tools
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to discover keywords related to your topic, including data on search volume, competition, and variations.
Enter a seed keyword related to your blog into the tool. For example, if your blog is about gardening, you might start with “gardening.â€
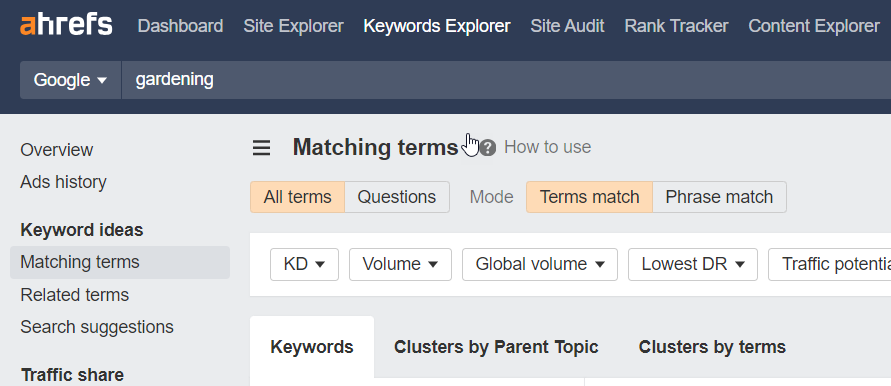
The tool will display a list of related keywords, and data on search volume, competition level, and sometimes even the average cost-per-click (CPC) for paid ads.
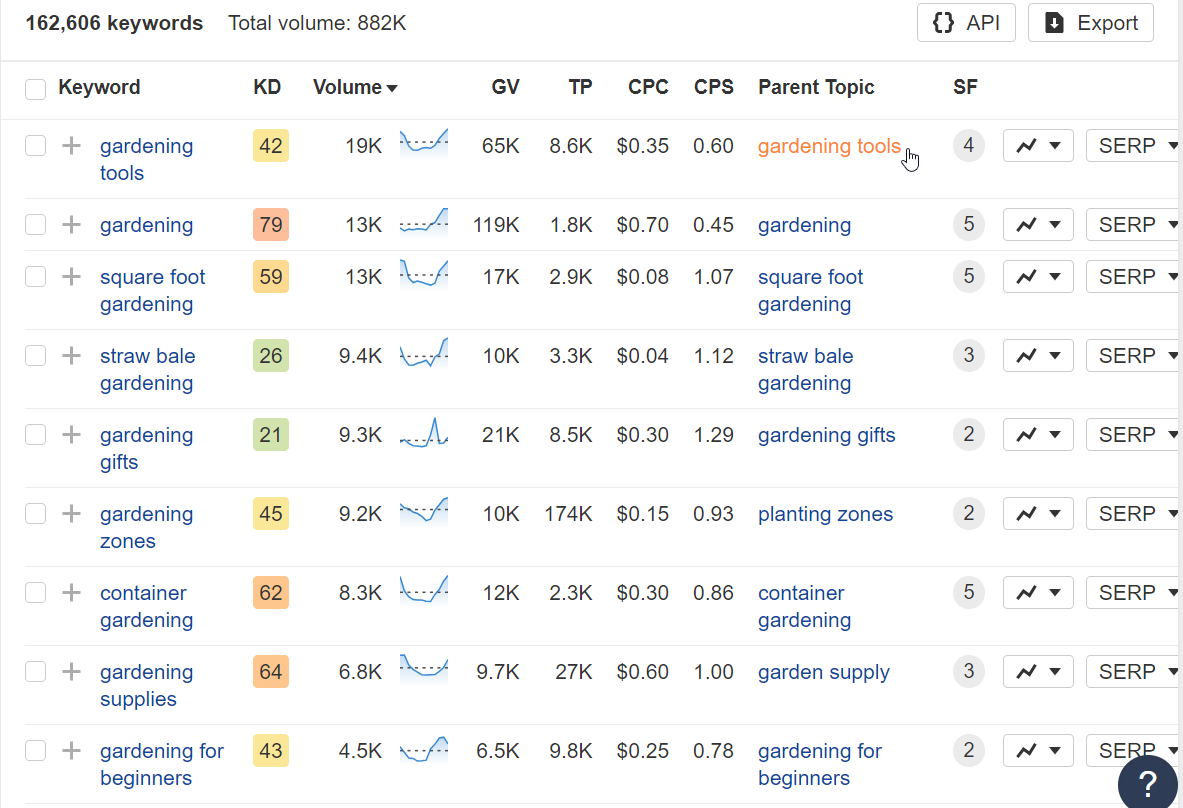
Use filters to narrow down the list. Look for keywords with decent search volumes but lower competition or keyword difficulty (KD). Also, consider the relevance and search intent behind each keyword.
For example, in this case, you can start with a post about “gardening gifts†since it has the lowest competition but a high search volume.
Pro Tip: If your blog is new, prefer to start with long-tail keywords. They often have lower search volumes and can rank faster on search engines.
Review Competitor Content to Find More Keyword Ideas
Start by identifying blogs or websites that rank well in your blog niche.
Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to get insights into your competitors’ keyword strategy.
Enter their URLs into these tools to see which keywords they rank for, the volume of traffic these keywords bring, and how they rank in search results.
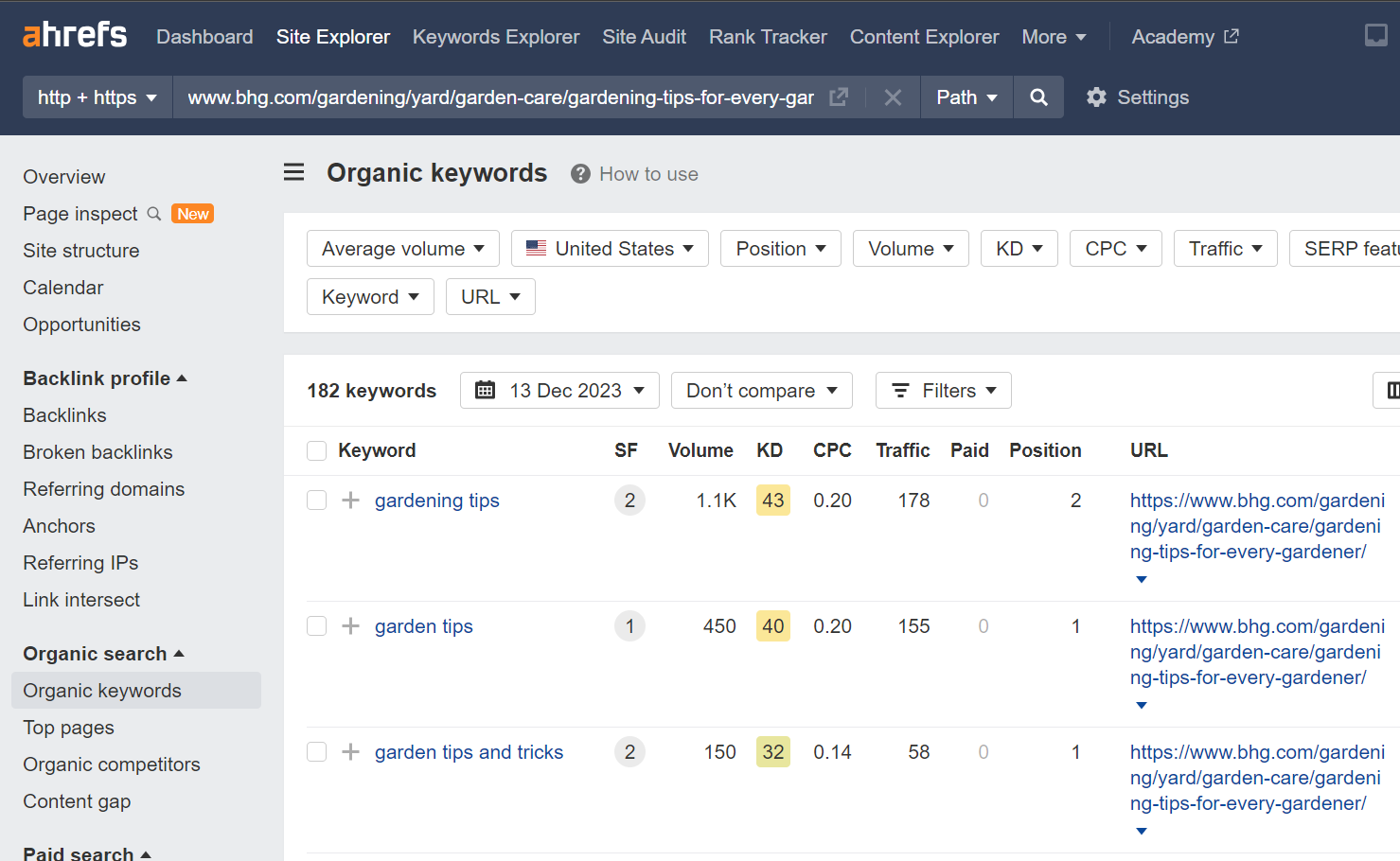
Remember, the goal isn’t to copy what your competitors are doing but to learn from their successes and oversights to refine your content and keyword strategy.
Compile a list of your primary keywords and their respective search volumes from the keywords you’ve identified.
Learn more about how to do keyword research for SEO
2. Organize Keywords by Topic Clusters
Topic clusters refer to a content marketing and SEO approach where you create content around a central topic (known as “pillar†content) and link it to related subtopics (known as “cluster†content).
This method is used to organize a website’s content structure more effectively and improve its SEO performance.
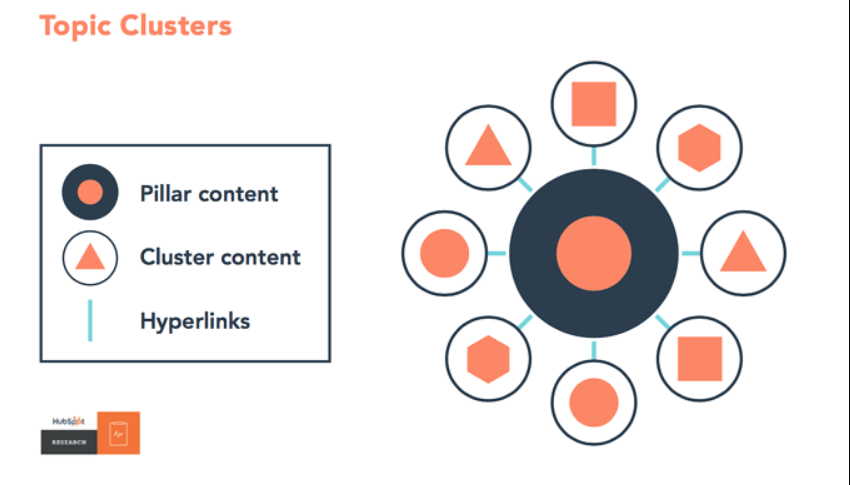
Source: Hubspot
Topic clusters reflect the way modern search engines like Google interpret user queries and content relevance.
Clusters effectively signal to both search engines and users that your blog is a reliable, authoritative source of information in your niche, strongly supporting your blog’s E-E-A-T profile.
Learn how to create topic clusters:
- How to Use Topic Clusters for SEO and Drive More Traffic To Your Website
- Topic Clusters for SEO: What They Are & How to Create Them
- How to Build a Topic Cluster in 10 Minutes
- Topic Clusters: The Next Evolution of SEO
3. Determine the positioning of your blog post
Positioning is the “angle†the writer will take for the target blog post. The best positioning will address the reader’s specific pain points and what information they want the most, as well as how it can best be structured to be most useful to the reader.
You will see the positioning in the SEO titles of the pages that are ranking in the top 10 of your target keyword.
For example, if you search “best gardening toolsâ€, virtually all results will be titled “best gardening tools [Year]â€.
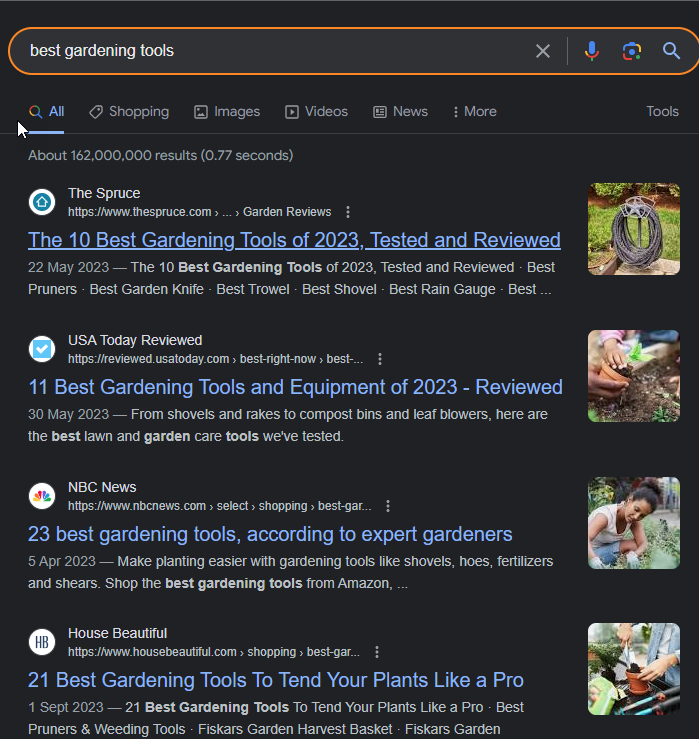
That means that recency is a very strong position in this case, as people want to see the most up-to-date list.
Or, if you search the keyword “how to make money onlineâ€, it will all be listicles with a certain number of ways to make money online.
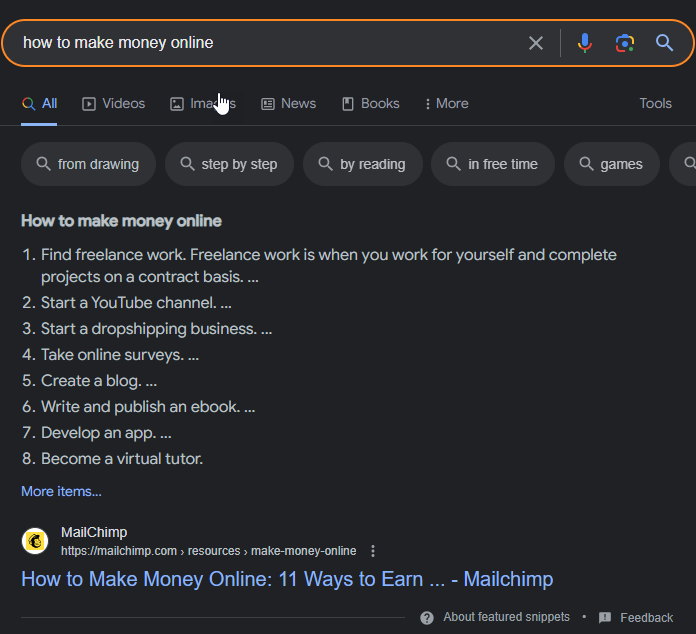
When you see that all articles have the same positioning like “Best Gardening Tools†[year] or [X] Ways To Make Money Online, that usually means that is going to be a very strong positioning.
However, simply copying the existing positioning likely will not work, especially if the other websites are more established websites than yours.
In this case, you have two options:
1. You can try to “leapfrog†the competition’s positioning, such as having a longer listicle on ways to make money online or adding the month or week you’ve updated the best gardening tools article.
2. You can try a completely different positioning by adding additional layer that makes your article more appealing.
For example, for the “How to make money online†article, you could still do a listicle, but make it a sortable list or have some other way you structure the content that makes it stand out.
4. Create Your Blog Post Outline with SEO in Mind
The main goal of content outlines is to organize and structure the content before the actual writing process begins. As well as provide specific SEO guidelines for that particular blog post.
Start by analyzing the search results and competitors for your main keyword.
Go to Google.com and search for the main keyword
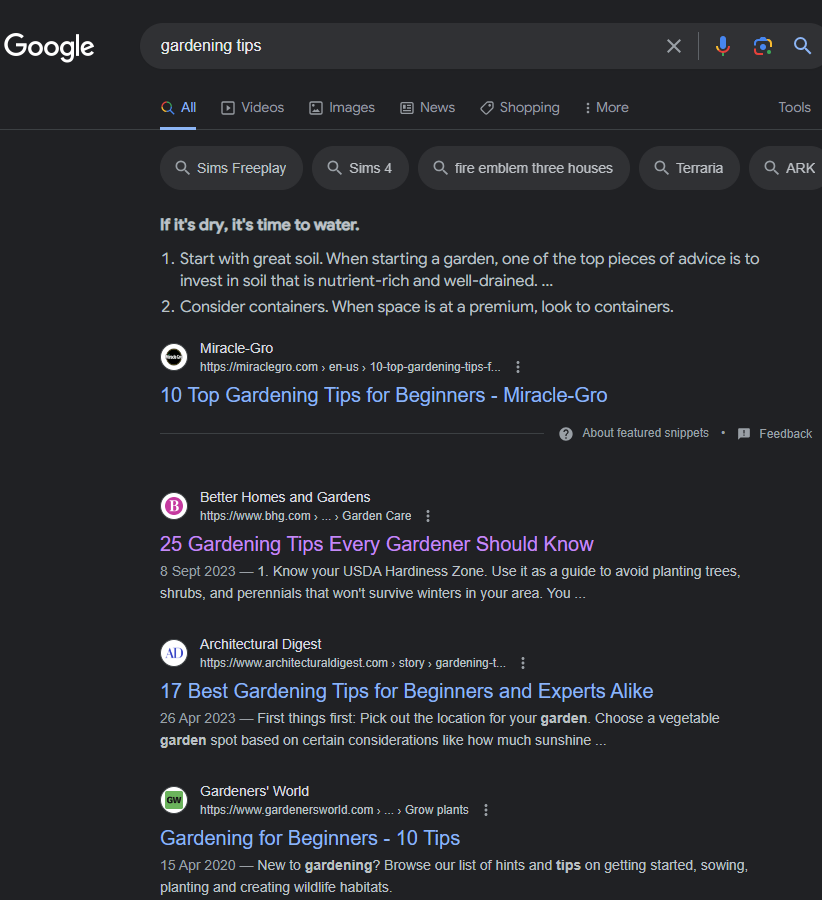
Skim through the SEO titles and take note of what is ranking.
- Are they blog posts?
- Product pages?
- How are they positioned?
- How are they structured?
Take a look at the subheadings.
- What do you see repeating?
- What do you think could be better?
You can also use AI tools like ChatGPT to identify some of the biggest pain points for searchers using the following prompt:
Act as an SEO expert. What are likely the biggest pain points for someone searching for the keyword “[keyword]?â€
This will give you some great ideas for subheadings, topics to cover, and how to position the article.
Pro Tip: Look at paid ads when creating an outline and searching for subheading ideas. The ad that is shown at the top was optimized to perfection, it contains important information you can use in titles, paragraphs, and tables.
Brainstorm the main sections of the article using H2s, H3s, (and occasionally H4s)
Base your H2s and H3s on the positioning of the article, and the data from search results and competitors. You can also include the ideas you generated with ChatGPT.
We recommend brainstorming all the headings you want to include and then cutting down and rearranging them in the most logical and helpful way possible.
How to arrange subheadings in the most logical and helpful way?
- Aim to answer the main search intent as fast as possible – typically the first H2. Do not bury the hook!
- The more important a section is, the higher up in the article it should be.
Hierarchy of Subheadings:
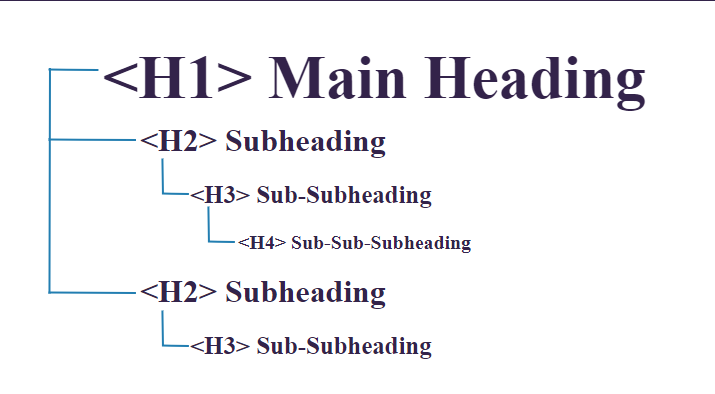
Source: brandextract.com
- Start with H1 for the blog post title. This should only be used once per page.
- Use H2 for major section headings. They can be seen as the main subtopics under the main title.
- H3 is for sub-sections under H2, and the pattern continues with H4, H5, and H6. However, most blog posts will typically only need up to H3 or H4.
Additional tips for creating subheadings:
- Make subheadings descriptive—A reader should get an idea of the section’s content just by reading the subheading. This helps users who skim content to find the information they’re looking for.
- Keep Them Concise—Subheadings should also be relatively short and to the point. Lengthy subheadings can disrupt the flow of an article.
- Maintain Consistency—If you start with action verbs or questions in your subheadings, try to maintain that style throughout. Consistency aids readability and looks more professional.
- Enhance Readability—Break up long paragraphs with subheadings to make the content more digestible. This especially helps mobile readers, as large blocks of text can be daunting on smaller screens.
- Use Them Strategically—Not every few lines need a subheading. Use them to introduce a new idea or section, not just for the sake of it.
- Styling—Bold, italics or different colors can be used to make subheadings stand out, but be consistent with your styling choices throughout the post.
Learn more about how to create a content outline: Content Outlines: How to Write Better Content Faster
5. Write The Meta Title and Page Title
The meta title (also known as SEO title) is what appears as the clickable link in search engine results pages (SERPs). It’s an opportunity to create a concise and compelling page content description while strategically incorporating target keywords.
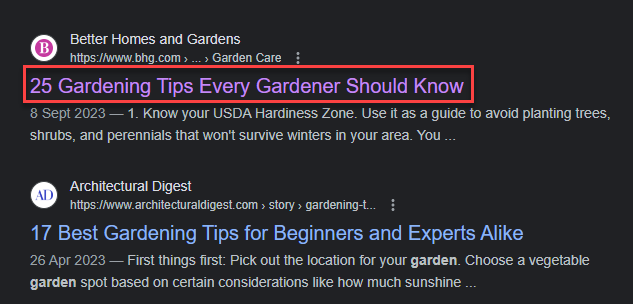
A page title is the H1 title of an article. It denotes the most important heading on a webpage.
Both titles should be carefully crafted to accurately represent the content and context of the page, while also considering SEO best practices to improve search rankings and user engagement.
Form an SEO title using the format:
[ROOT KEYWORD] + [POSITIONING]
For example,

In this example:
- Golden Retriever Pros & Cons is the main keyword
- Is one right for you? is the first positioning
- expert tips is the second positioning
The length of the title is determined by pixels and not characters. You can use the Snippet Optimizer Tool to determine the right amount of pixels.
Additional tips:
- Get creative with shortening and using lower case versus uppercase letters such as “w/†instead of “with†or “&†instead of “andâ€
- Use parenthesis if possible to increase click-through rate (& drive curiosity!)
- Do not include the company name in the title. This is almost always weak positioning unless your brand is extremely well known.
Here are some examples of great SEO Titles:
- 43 Best Travel Jobs 2024 (w/ Salaries & Pros + Cons)
- 77 Best Businesses To Start W/ 10K Or Less (& how to pick one)
- 27 Legitimate Jobs for Stay-at-Home Moms in 2023 (Earn Fast!)
- Buying a House in Recession: Pros, Cons, and Expert Advice
- How To Find All My Debts (& Pay Them Off)
- Types of Bank Accounts: How To Set Them Up & What To Avoid
How to craft the page title
The page title will essentially be the same as the SEO title, without the restrictions of space so you can do stuff like write “with†instead of “w/â€.
6. Place Keywords Strategically Throughout the Blog Post
Strategically placing keywords throughout a blog post is crucial for SEO. Here are the best places to include them:
- Title (H1 Tag)—The main title of your blog post should contain your primary keyword. This is the first thing search engines and readers see.
- SEO title: A well-crafted meta title with appropriate keywords can make your post more appealing to users and increase click-through rates.
- First Paragraph: Incorporate the primary keyword naturally in the opening paragraph to reinforce the topic early on.
- Subheadings (H2, H3 Tags): Use keywords in subheadings to break up the content and make it more scannable for both readers and search engines.
- Body of the Content: Sprinkle primary and secondary keywords naturally throughout the body. Aim for a natural flow; avoid keyword stuffing.
- Image Alt Text: If your blog post contains images, include relevant keywords in the image alt text. This improves image search visibility and accessibility.
- Call to Action: If applicable, use keywords in your call to action at the end of the post.
Subheadings are one of the best places to naturally incorporate primary, secondary, and LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords. Make sure to use them liberally in your subheadings.
This emphasizes the importance of keywords to search engine crawlers and can help with ranking.
Pro Tip: Use keywords and synonyms instead of reference words (e.g. this, that, etc.) whenever possible as long as they flow naturally. This makes it easier for Google to understand
For example, “Things You Need to Know When Starting a Businessâ€, NOT “Things To Keep In Mindâ€.
7. Include Call-to-Actions (CTAs)
Call-to-Actions (CTAs) are prompts or instructions designed to encourage an immediate response or sale from your blog readers.
CTAs guide your audience toward the next step, be it subscribing to a newsletter, downloading a resource, making a purchase, or any other desired action.
Creating an effective CTA involves clear, concise, and action-oriented language that stands out visually. It should be easily identifiable, often through contrasting colors or distinct buttons.
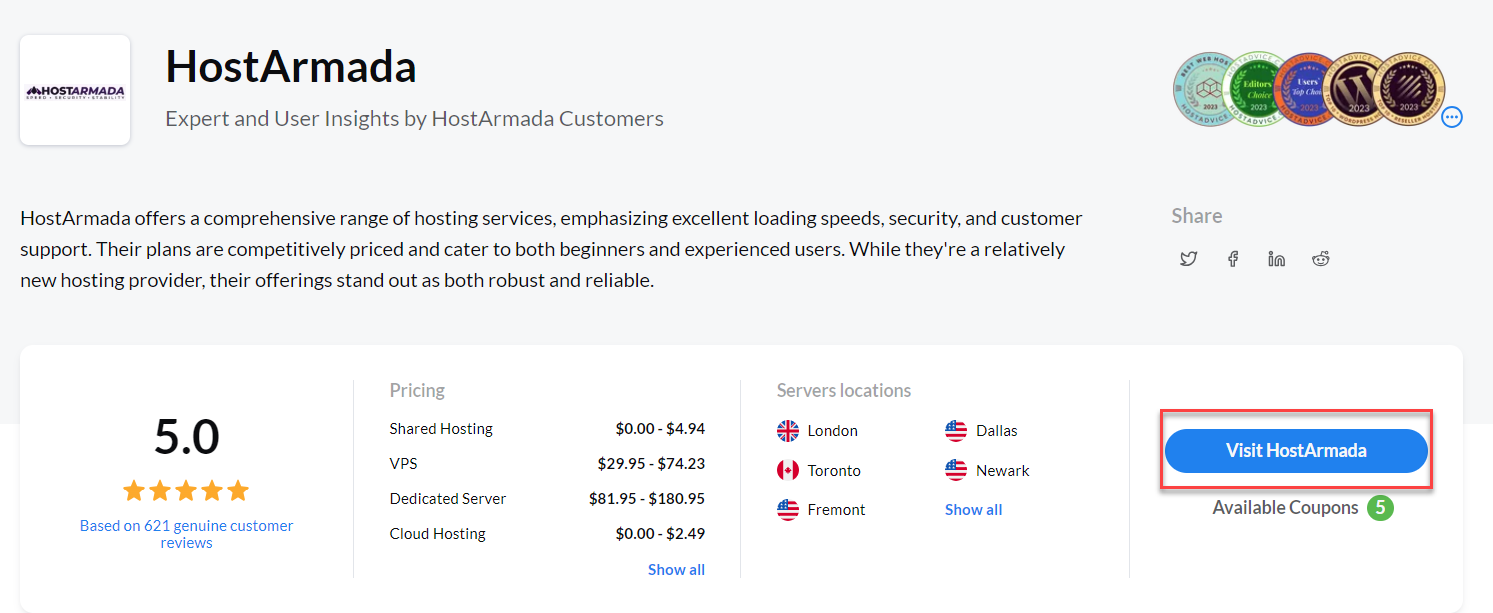
In a blog, for instance, a CTA might be at the end of a post suggesting further reading or subscription
On a product review page, it might be a prominent “Visit Website†or “Add to Cart†button.
Pro Tip: The blog conclusion can include a summary or CTA.
For example: Final Word: What is right for you? Make a decision
8. Prioritize the Reder’s Engagement
The primary goal of focusing on the reader’s experience and engagement is to create a satisfying, informative, and enjoyable interaction for your blog audience.
A positive reader experience builds a loyal readership, enhances brand reputation, and ultimately drives conversions.
Good user experience also contributes to lower bounce rates and longer session durations, which are positive signals to search engines and can improve SEO rankings.
Factors Affecting User Experience
Intuitive Navigation: Help readers find desired content quickly and easily.
Page Loading Speed: Fast loading times are crucial for keeping visitors from leaving your blog prematurely.
Learn more about improving your blog’s loading speed:
- How to Make a Website Faster: Enhancing Performance and User Experience
- Exploring Website Load Time Statistics: Key Metrics & Insights
- WordPress Speed Optimization: 23 Ways to Speed Up Your WordPress Site
- 10 Reasons Why Your Website Won’t Load (and What to Do about It)
Readability: People don’t start by reading; they evaluate the page as a whole, and if they see something that interests them, they will start reading.
To employ scannable content, use short paragraphs, bullet points, subheadings, and a table of contents.
Other Factors Include:
- Formatting: Consistently format your posts for a professional look, using headers, lists, tables, and bold text to highlight key points.
- Relatability: Start a new blog post by relating to the reader. A good way of doing that to start with 1-2 questions that highlight the journey and pain points of the reader.
- Content difficulty: Write content at a 9th-grade reading level to ensure it’s easily understood by a wide audience.
Pro Tip: Use analogies and examples to emphasize your point and make the content more relatable.
9. Add SEO-Optimized Visuals
Visuals make content more captivating and comprehensible, breaking up text and clarifying concepts, which in turn supports better search engine rankings.
They also cater to diverse audiences, including people with visual processing preferences or reading difficulties, broadening the reach and inclusiveness of your content.
Best practices for incorporating images
Here are several best practices for using images to enhance user experience and SEO.
Include at least 1 relevant featured image—A featured image is the main image associated with a blog post. It usually appears at the top of a post and also when the post is shared on social media. An SEO-optimized featured image needs to address the search intent and include the page title text.

Other Image SEO best practices:
- Image Licensing and Attribution—Use images that are properly licensed, and if required, provide appropriate image attribution. Unsplash.com and Pexels can be great resources.
- Image Filename—Use descriptive filenames for images that include relevant keywords. Separate words with hyphens for better readability. For example, “seo-friendly-image.jpg“.
- Image Alt Text—Always include descriptive and meaningful alt text for each image. Use keywords when appropriate, but keep it natural and relevant to the image. We’ll elaborate more on alt text below.
- Image Size and Compression—Large images can impact page load speed. Compress images to reduce file size without losing quality. You can use tools like Adobe Photoshop, or TinyPNG.
- Image Format—Choose the appropriate image format based on the type of image. For example, JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics with transparency.
- Image Captions—Add captions to images when applicable, as they can provide context and additional information. Include relevant keywords in image captions but avoid overstuffing.
- Image Placement—Position images close to the relevant text to enhance their contextual relevance. Avoid placing important text within images; use HTML text for important content.
10. Write a Descriptive Image Alt Text
An image alt text, short for “alternative text,†is a descriptive text attribute added to an image tag in HTML. It’s a fundamental aspect of web accessibility and blog SEO best practices.
Always include descriptive and meaningful alt text for each image. Use keywords when appropriate, but keep it natural and relevant to the image.
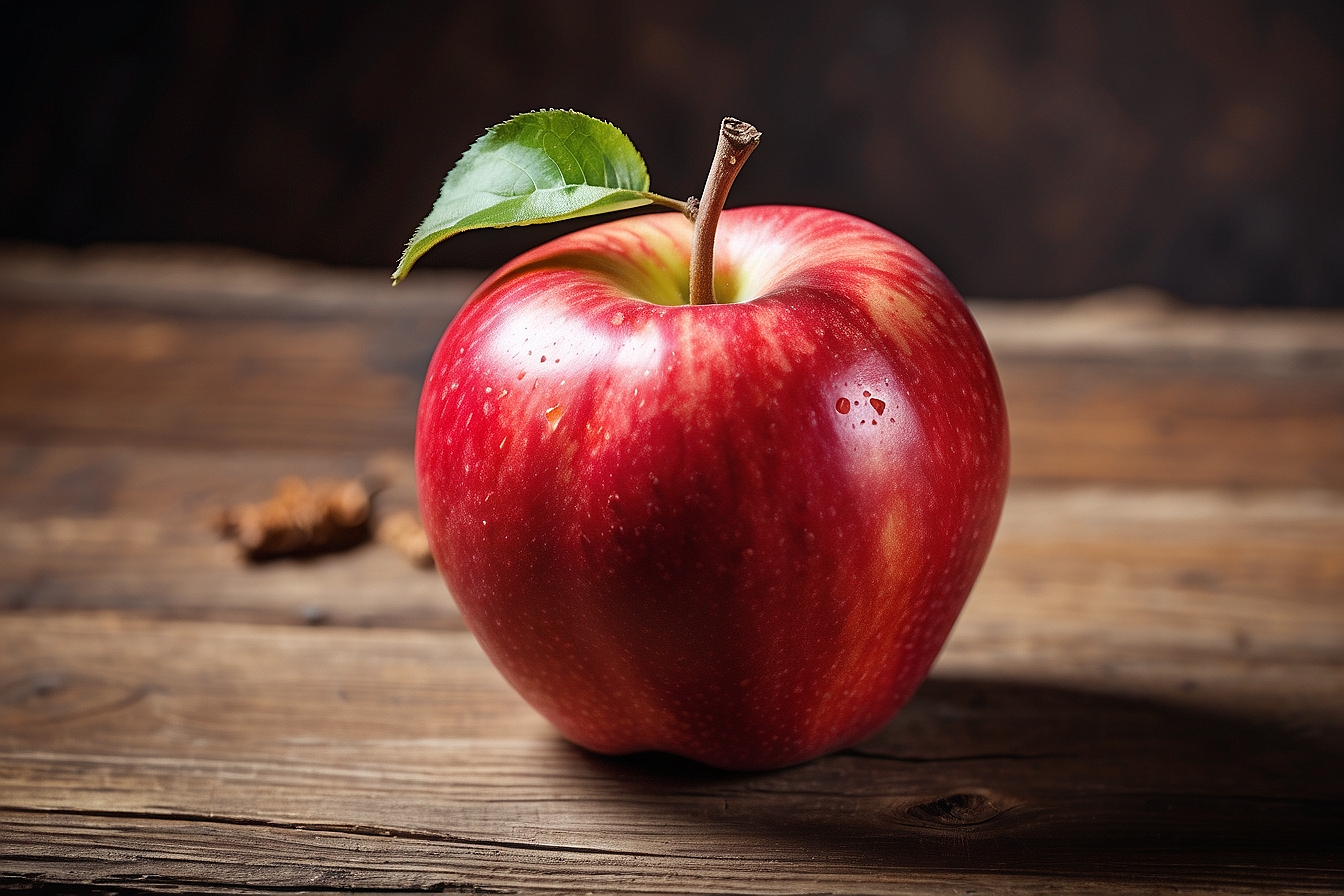

The alt text of the above image would be “Fresh red apple resting on a rustic wooden tableâ€.
In this example, the alt text provides a clear and concise description of the image’s content. It conveys essential details, such as the object (apple), its color (red), and its location (wooden table).
This alt text would be helpful for both visually impaired users relying on screen readers and search engines indexing the image. It avoids unnecessary words, provides relevant information, and accurately represents the image, making it a good example of alt text.
11. Optimize for SERP Features
A SERP Feature is any result on a Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) that is not a traditional organic result.
These features are designed to provide users with direct, specific information and often appear more prominently than standard listings.
Most Common Types of SERP Features
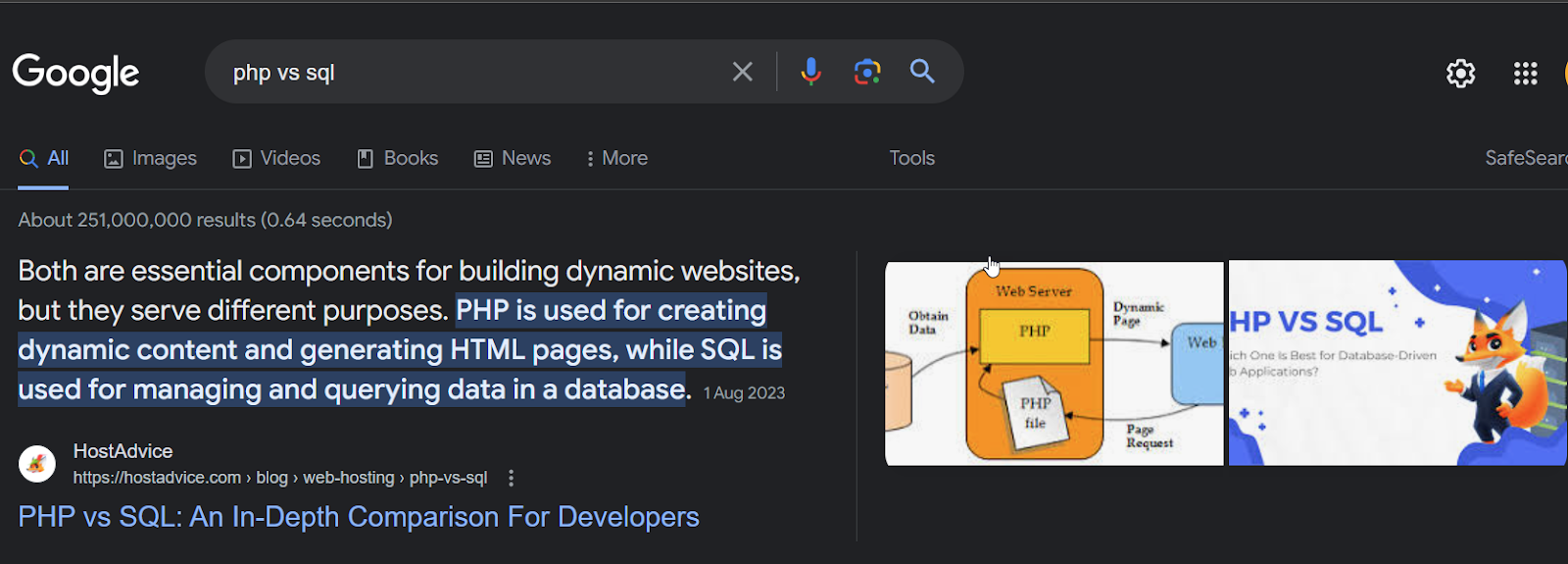
- Featured Snippets (position zero): These are short excerpts that appear at the top of SERPs, directly answering a user’s query. They pull information from a webpage and display it in a box, along with the page’s title and URL.
- People Also Ask Boxes: These boxes contain a list of related questions to the initial search query.
- Knowledge Panels: Displayed typically on the right side of SERPs, these panels provide concise, authoritative information about entities like celebrities, organizations, places, or events.
- Image Carousels: For queries that are best answered with images, Google displays a horizontal scrollable carousel of images at the top of the search results.
Example of a featured snippet
SERP Features Statistics:
- Featured snippets received 35.1% of all organic clicks.
- People also ask boxes receive only 6% of all clicks.
- Featured snippets and knowledge panels recieve 42% of the total click share.
How to Optimize for SERP Features
- Winning Google SERP Features: How to Optimize for Visibility
- How to optimize your content strategy for Google SERP features
- What are SERP Features? (And How to Get Them)
12. Include Internal Links to Other Blog Posts
An internal link is a hyperlink that connects one page of a website to a different page within the same website.
Internals link best practices include:
- Showcase the depth and breadth of your content by linking to highly relevant blog articles.
- Make sure the linked articles provide additional context or valuable information to the reader.
- Use descriptive and natural anchors that accurately represent the content of the linked article.
- Avoid using generic phrases like “click here†or “read more.â€
- Avoid overloading the blog post with too many internal links; use them judiciously.
- Diversify linked content: Link to a variety of blog articles throughout your website, covering different aspects of the topic.
- Provide a brief context or teaser about the linked article to encourage readers to click on the link. This can be done within the blog post’s text or in a related section like “Further Reading.â€
Example 1:
Anchor Text: “Learn more about on-page SEO techniquesâ€
In this example, the anchor text “on-page SEO techniques†is descriptive and specific, providing a clear indication of what the linked page is about. It encourages readers to click on the link to gain further knowledge about the topic.
Example 2:
Anchor Text: “Check out our latest guide on SEO Content Strategiesâ€
In this instance, the anchor text “SEO content strategies†is direct and compelling, enticing readers to click on the link to access the recently published guide. It accurately represents the content of the linked page and encourages user engagement.
13. Create User-Friendly URL Slugs
A URL slug is the part of a URL that identifies a specific page on a website in a form readable by both users and search engines.
It usually comes at the end of the full URL and is typically a few words long, representing the content of the page.
For example, in the URL “www.example.com/blog/how-to-grow-tomatoesâ€,
The URL slug is “how-to-grow-tomatoes.â€
This slug indicates that the content of the page is about growing tomatoes.
Tips for creating user-friendly URL slugs
- Keep It Relevant—The URL slug should provide a clear idea of what the reader can expect from the page. Avoid using vague or misleading slugs that don’t match the content.
- Match Page Title—Ideally, your URL slug should be closely related to your page title. Consistency between the title, content, and URL helps with SEO and user trust.
- Use Target Keywords—Incorporate relevant keywords that describe the main theme of the article. Keywords can help search engines understand the content.
- Do Not Use Positioning—Never include positioning in a URL slug, as positioning may change over time. For example, 11 gardening tips can become 13 gardening tips.
- Be Descriptive and Concise—Aim for a concise URL slug that conveys the essence of the article. Shorter URLs are generally preferred, as they are easier to read and share. Remove unnecessary words like “and,†“the,†“of,†etc.
- Use Hyphens for Spaces—Use hyphens (“-“) to separate words within the URL slug. Search engines consider hyphens as word separators, making it easier to read for both search engines and users. Avoid underscores (“_â€) or other special characters.
- Avoid Stop Words—Stop words are common words like “a,†“an,†“the,†“in,†“on,†etc. These words don’t add significant value to the URL and can be omitted to create a cleaner slug.
- Exclude Dates and Numbers—If your blog article is evergreen, exclude numbers and any type of year or month in the URL slug. This maintains the relevance of the article over time.
- Avoid Duplicate Slugs—Each URL on your website should have a unique slug. If you have multiple articles on similar topics, differentiate their slugs to prevent confusion.
- Use Lowercase Letters—URLs are case-sensitive, but it’s a good practice to use lowercase letters for consistency and to avoid confusion.
Examples:
Topic: Healthy Breakfast Recipes
URL Slug: /healthy-breakfast-recipes
Topic: Tips for Time Management
URL Slug: /time-management-tips
Topic: Guide to Starting a Vegetable Garden
URL Slug: /starting-vegetable-garden
14. Update Existing Content
Search engines favor fresh content. A HubSpot survey found that updating and republishing old blog posts can increase organic traffic by as much as 106%.
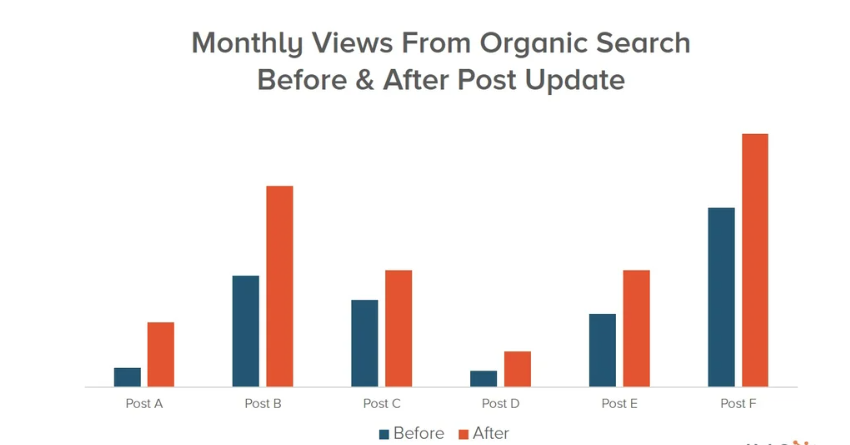
Ahrefs team found that after updating an old blog post, the traffic to that post doubled overnight and kept climbing.
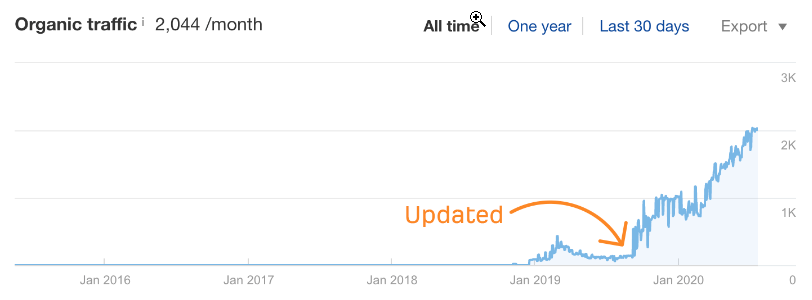
Source: Ahrefs
Pro Tip: Not all blog posts are worth updating. Focus on updating blog posts that had 20+ monthly visitors at their peak, as they significantly contribute to overall organic traffic growth, unlike posts with fewer pre-update visitors.
To identify outdated or underperforming posts, start by conducting a content audit.
Once you’ve identified which posts are worth updating, you can take the following steps:
- Refresh any outdated facts, statistics, and links
- Improve the readability and quality of the content
- Add new sections or content that address related topics or recent developments
- Research and integrate new or missing keywords into subheadings and body.
- Replace or add new images, graphics, or videos that are more relevant to the updated content.
Learn more about how to update existing content:
- Republishing Content: How to Update Old Blog Posts for SEO
- Content Refreshing: A Step-by-Step Strategy
- How to Update Old Blog Posts and Republish Content
15. Build Backlinks
Backlinks are links from one website to a page on another website. They act as a vote of confidence from one site to another. Each backlink tells search engines that other sites find your content valuable enough to link to.
The main goal of backlinks is to boost domain authority, increase traffic, and increase the credibility and trust of your blog.
The most common backlink strategies
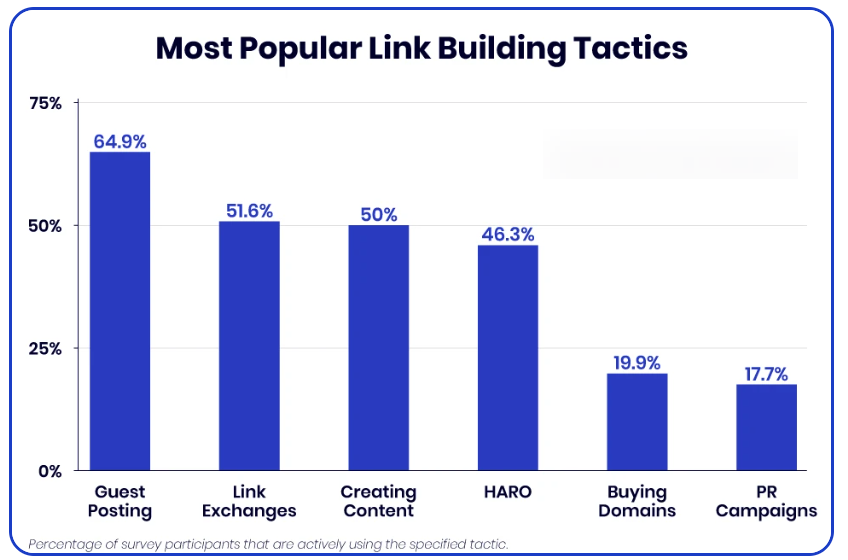
Source: Authority Hacker’s survey
- Guest Posting—Publish articles on other websites with a backlink to your blog.
- Link Exchanges—Engage in reciprocal linking where you and another site agree to link to each other’s content. Choose high-quality partners to avoid any negative SEO impacts.
- Creating Shareable Content—Develop content that is informative, engaging, and offers value such that other sites want to link to it.
- Utilizing HARO (Help A Reporter Out)—Respond to queries from journalists and bloggers via platforms like HARO.
- Buying Domains—Acquire domains with existing authority and redirect them to your site.
- PR Campaigns—Get featured in news articles, interviews, and other media outlets.
There are many other strategic methods to acquire high-quality backlinks such as the Skyscraper Technique, Broken Link Building, and Resource page link building
Learn more about link building:
- How to Get Backlinks: 14 Tactics That Work
- Link Building Strategies: The Complete List
- 77 Link Building Strategies for SEO in 2024
- Link Building Strategies: Enhancing Your Website’s Credibility and Reach
16. Optimize for Mobile Devices
Mobile internet traffic accounts for almost 60% of web traffic worldwide. In the first quarter of 2023, mobile devices generated 58.33 percent of global website traffic,
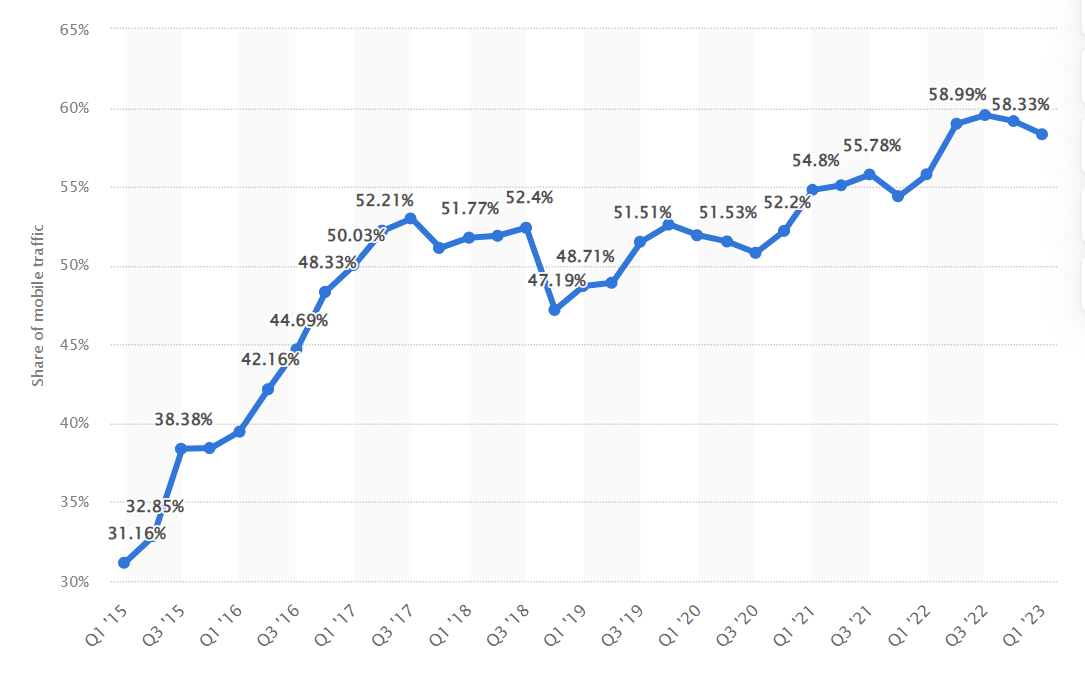
Source: Statista
The global number of mobile internet users is expected to continuously grow between 2024 and 2028 by 219 million users (+3.38 percent).
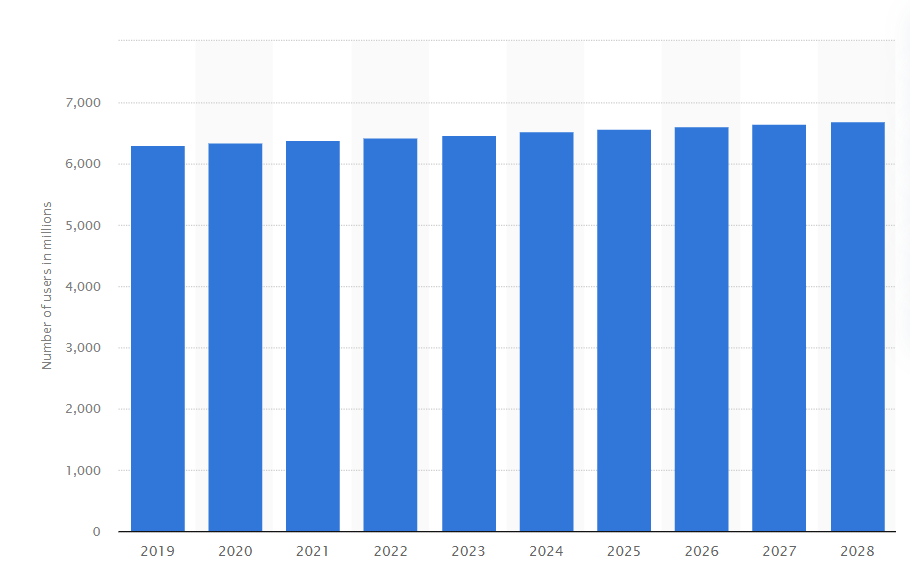
Source: Statista
In the past, Google’s indexing system primarily used the desktop version of a website to evaluate its relevance to users.
In 2016, Google announced mobile-first indexing. By 2018, over 50% of websites had shifted to mobile-first indexing.
In May 2023, Google announced that the switch to mobile-first indexing was completed.
This change means websites not optimized for mobile devices may see a decline in their search rankings.
Learn how to improve your mobile site:
- 10 Tips For Making A Mobile Friendly Website
- How to optimize your site for mobile devices
- 10 Optimization Tips to Build a Mobile-Friendly Site
- How to improve your mobile site?
17. Monitor Technical SEO Issues
To enhance your site’s technical optimization, consider the following aspects:
XML sitemaps
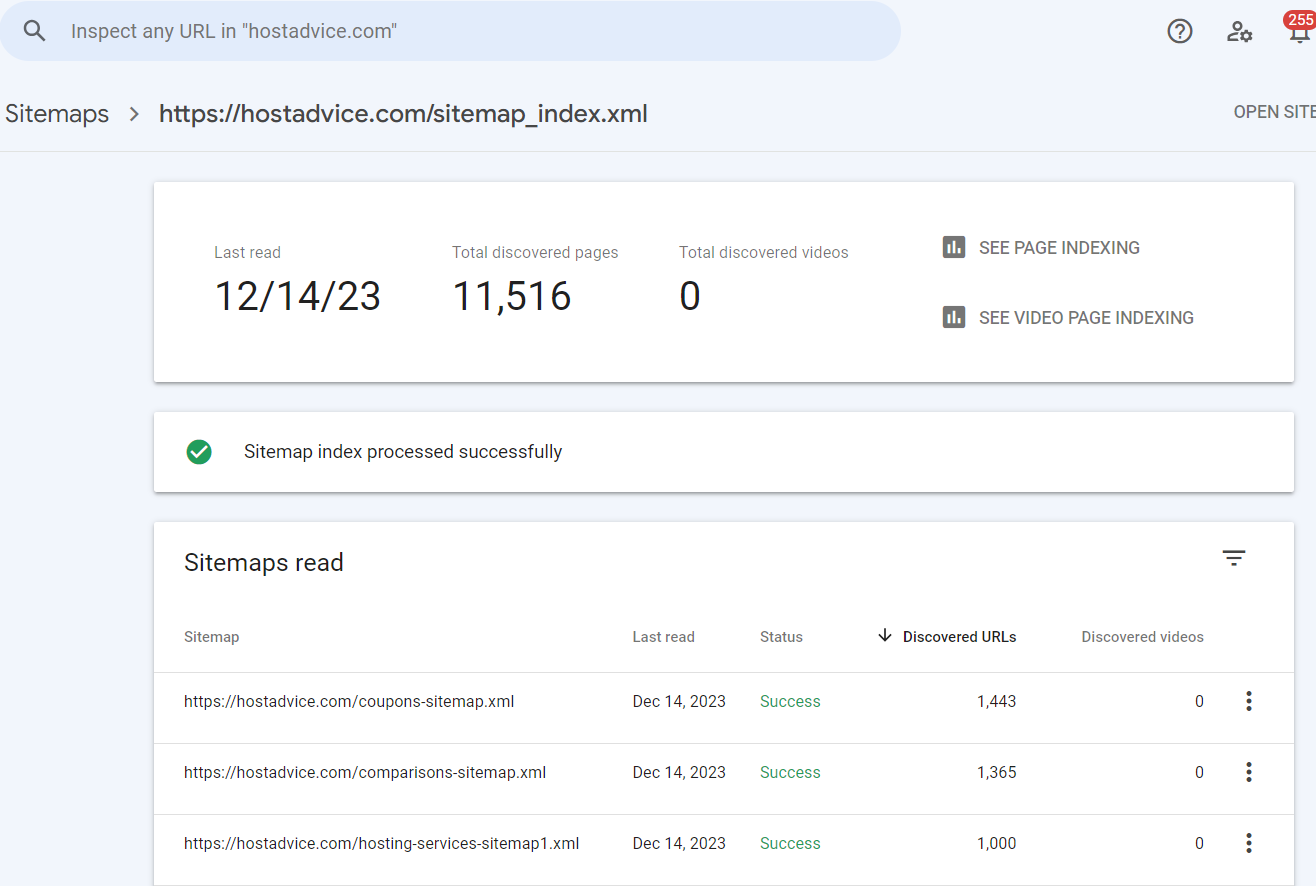
An XML sitemap helps search engines understand the structure of your site.
You can ensure your sitemap is updated and free of errors with tools like What Is Google Search Console: Optimizing Your Website’s Search Presence.
Head over to the “Sitemaps†feature in GSC
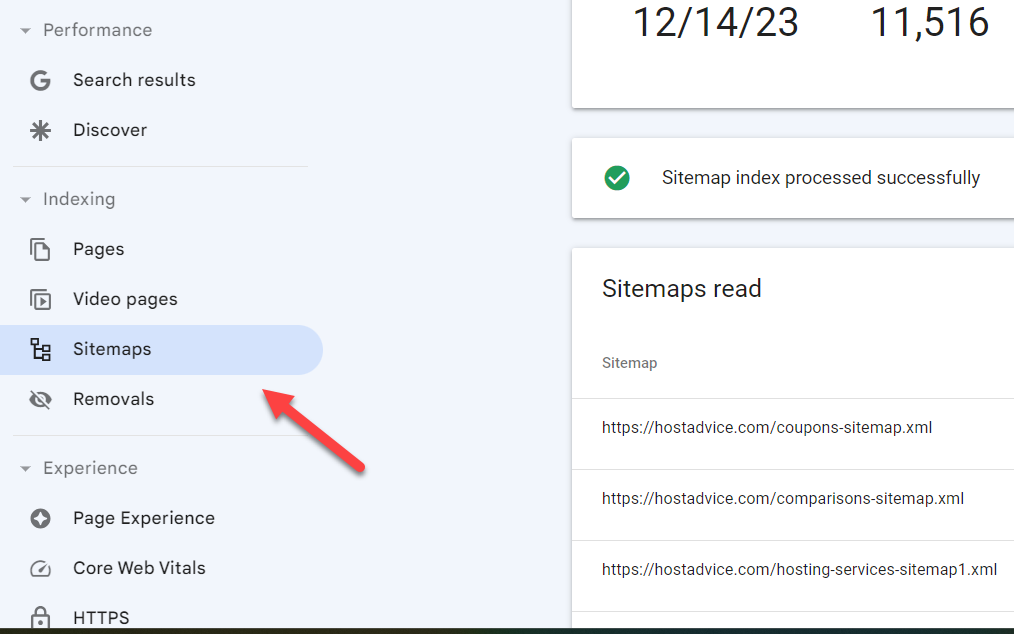
This feature allows you to see if your blog’s sitemap has any issues.
Site architecture
A clear structure helps search engines understand your site’s layout and the relationships between different pages, which can positively impact your search rankings.
For small sites, prefer a flat structure. In a flat site structure, most pages are just a few clicks away from the homepage.
It makes it easier for search engines and users to access most pages with minimal navigation. It can also distribute page authority more evenly across your site.
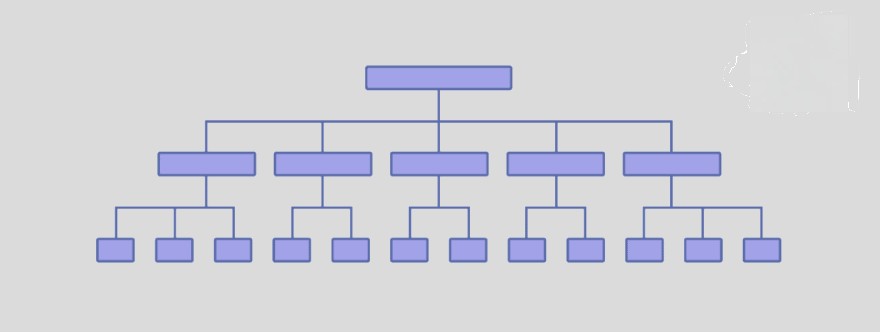
Source: Backlinko
For larger sites with a vast amount of content, prefer a more hierarchical, deep structure.
This involves categorizing content into directories and subdirectories. While deeper structures can make certain pages less immediately accessible, they allow for more organization and segmentation, which is crucial for large sites with diverse content.
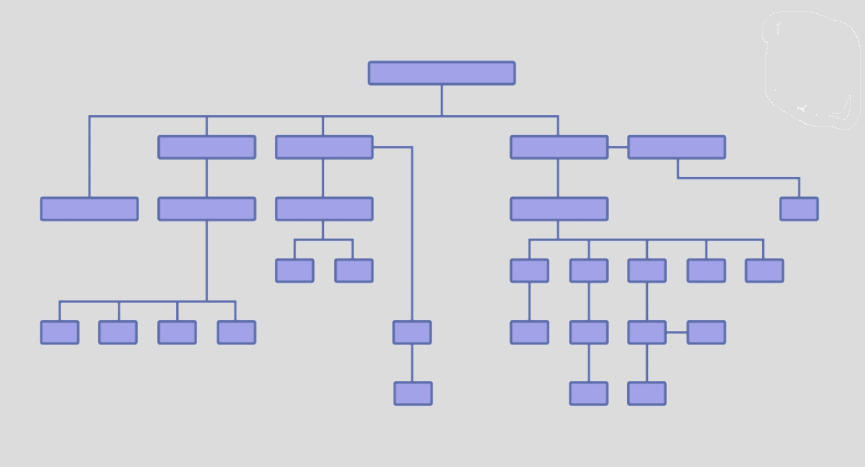
Source: Backlinko
Canonicalization
Canonical tags are HTML elements that prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the “preferred†version of a web page.
Canonical tags guide search engines to index and rank the “preferred†version and ignore the other version of the page.
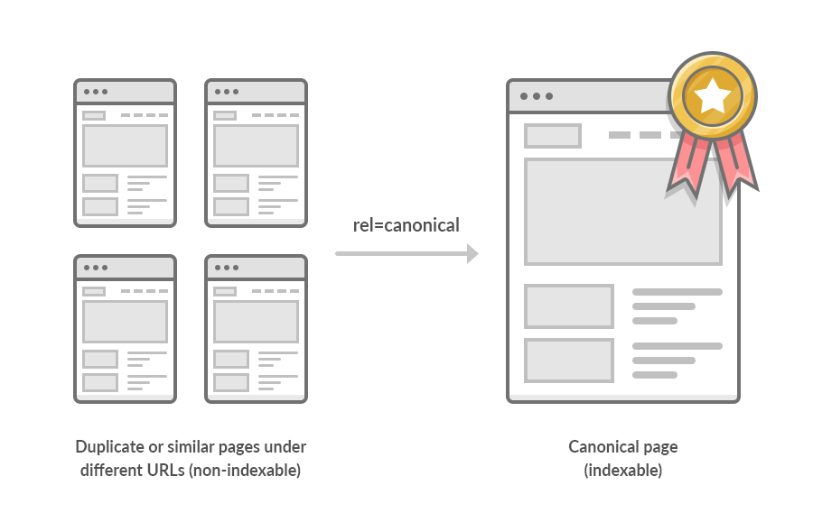
Source: Ahrefs.com
A canonical tag appears in the head section of an HTML document. The syntax looks like this:
<link rel=â€canonical†href=â€https://www.example.com/preferred-page.html†/>
Other use cases of canonical tags include:
- Preventing Issues with URL Parameters—Tracking or sorting parameters can create seemingly different URLs with the same content.
- Handling HTTPS vs. HTTP and WWW vs. Non-WWW Versions—Avoid duplicate content issues by specifying your preferred domain format.
- Cross-Domain Content—Canonical tags can indicate the original source when the same content is legitimately published across multiple domains.
Covering all technical SEO aspects is beyond the scope of this article. To learn more about technical SEO optimization, read the following guides:
- What Is Technical SEO: Optimizing Your Website for Search Engines
- Technical SEO: The Definitive Guide
- The Beginner’s Guide to Technical SEO
- What’s technical SEO? 8 technical aspects everyone should know
Final Word: Master the Art of Blog SEO Optimization
Effective blog SEO involves a blend of strategies, from optimizing content and visuals to addressing technical SEO aspects.
Remember, consistently applying these tips can significantly boost your blog’s search engine presence.
For further enhancement, explore our recommendations on the best web hosting providers for SEO and best website builders for SEO. Dive deeper into these tools to truly master the art of blog SEO optimization and elevate your online presence.
Next Steps: What Now?
- Use tools like Google Analytics and Search Console to track your blog’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Invest time in exploring SEO tools and platforms like Ahrefs and SEMRush.
- Consider switching to a hosting provider specializing in SEO-friendly services for better performance.
- Look into website builders known for their SEO capabilities to enhance your blog’s structure and accessibility.






