
Key Highlights
- E-commerce is transferring products, funds, and data over an electronic channel such as the internet.
- The e-commerce industry is expected to rise from $992 billion in 2022 to $2.9 trillion in 2026.
- The common types of e-commerce are Business to Consumer (B2C), Business to Business (B2B), and Consumer to Consumer (C2C).
- Creating an online store requires you to find a profitable, in-demand product, create a business plan, set up an e-commerce website and promote it.
- Wix, GoDaddy, Shopify, and Squarespace are some of the best e-commerce website builders.
Expand on the definition

E-commerce is short for electronic commerce. It generally refers to trading goods and services over an electronic channel like the internet. It also covers the transfer of data or funds over an electronic network. Other similar terms for e-commerce include e-tailing, online trading, and e-business.
E-commerce relies on the internet. Customers (direct consumers, businesses, or other entities) surf through online stores and marketplaces to search for and place orders for products and services via internet-enabled devices. This process often includes using a payment processor to receive payment which validates the order.
E-commerce platforms come in many types. They include independent online stores, online marketplaces where sellers sign up, and social media platforms where small-scale vendors connect with their customers to make sales.
Types of E-commerce
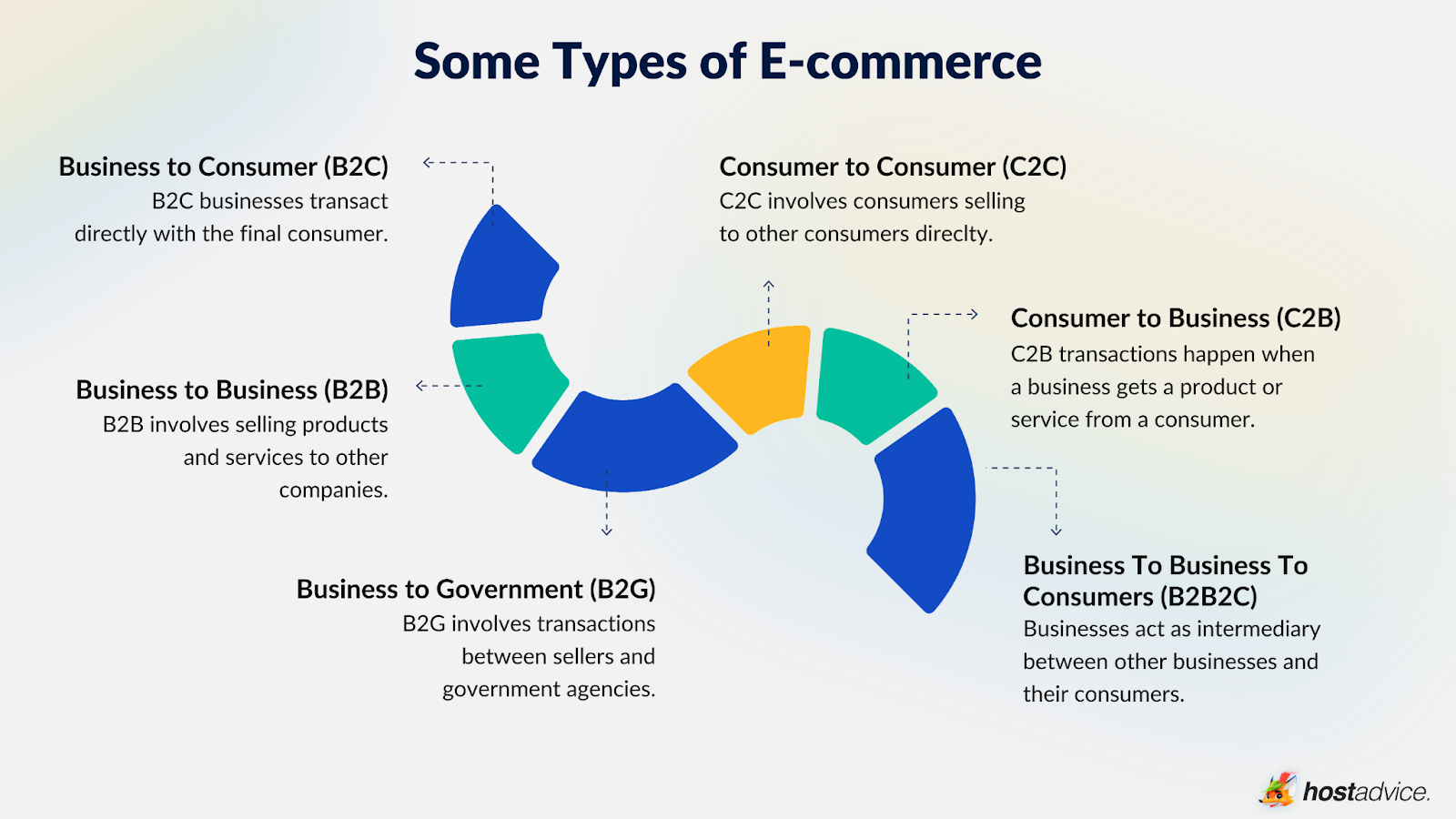
An e-commerce business could take different forms depending on the business model of the organization that adopts it. Here are the most popular types:
- Business to Consumer (B2C): B2C businesses transact directly with the final consumer. It is the most common type of e-commerce and likely what people think about when you mention e-commerce. Anyone can use this e-commerce type to sell products such as electronic devices or services such as website builders to create websites.
- Business to Business (B2B): B2B involves selling products and services to other companies. These transactions often involve longer lead times, larger volumes, and greater specifications. It could also be a recurring transaction if the buying company needs the goods for recurring manufacturing processes.
- Business to Government (B2G): This involves transactions between sellers and government agencies. B2G transactions typically involve rigorous processes and specific product or service criteria.
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C): Generally, only businesses can sell goods or services. However, with the rise of auction marketplaces and social media, many consumers can now list their products/services and make sales. These include auction-style listings on platforms like eBay and social media like Instagram and Tik Tok to sell directly to other consumers.
- Consumer to Business (C2B): C2B transactions happen when a business gets a product or service from a consumer or end user. The process may include soliciting feedback, crowdsourcing ideas, harvesting user-generated content, and buying customer ad space. The company gains marketing data and increased engagement and patronage while the consumer gets compensation via direct payments, full or partial discounts, or personalized service.
- Business to Business to Consumer (B2B2C): B2B2C is an e-commerce model where a business acts as an intermediary between other businesses and their consumers. This model is a collaborative process that combines business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C). In this sense, the first business partners with another business to deliver a product to the consumer.
Business Models in E-commerce
E-commerce businesses can adopt different business models based on the nature of their goods/services, operations, and target buyers. These business models have their unique manufacturing and shipping methods.
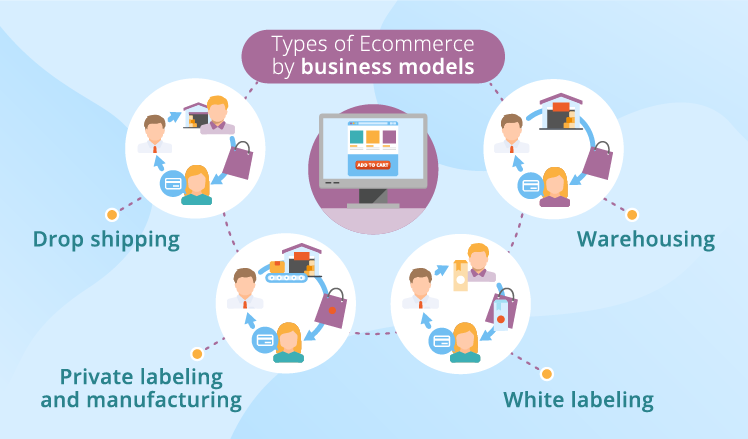
- Dropshipping: Dropshipping is a business model in which the seller only orders the goods/services they claim to sell when they have an order. They offer their products at a cost that includes the initial price (and sometimes delivery fee) and their expected profit. It is the least expensive e-commerce business model and perfect for people who want to avoid holding and managing inventory.
- Makers: The maker’s e-commerce business model happens when the seller makes the products/services. These can include fashion items or natural beauty products. The upside is that the seller has complete control over quality, branding, and availability. The downside is that the seller has to handle the manufacturing and warehousing process. It is ideal for people who enjoy crafting items and have the resources available.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing involves the large-scale production of goods. It has the highest financial investment requirement. The manufacturing business model for e-commerce comes in two categories: private label and white label. Private label manufacturing is when the manufacturer creates and sells the products to consumers directly. White-label manufacturing involves producing the products and letting retailers buy and rebrand them as their own. Private labels are ideal for unique products, while white labels work best for generic products.
- Wholesale: The wholesale business model involves buying goods from manufacturers in bulk and selling them to retailers and resellers. This model is a good option for those who want to deal with established brands and sell various products and brands. The downside is that the wholesaler has to purchase the inventory and store them in their warehouse until they get a buyer.
- Print on demand: The print-on-demand model offers made-to-order products based on unique designs. Like dropshipping, you only order the product from a printing partner when you have a buyer. The third-party printing service typically creates, packs, and ships the order.
- Digital products: A digital product is an online asset or multimedia that sellers can distribute online. These products are downloadable, streamable, transferable or all three depending on their name. Examples include PDFs, web content, NFTs, audio files, videos, templates, and plugins. You can make it a one-time sale, use a freemium model, demand monthly subscriptions, or offer licenses to use your digital products.
- Direct-to-consumer (DTC): The direct-to-consumer business model refers to how businesses sell directly to the final user without using third-party retailers like Amazon. It is common among all brands, from small startups to large ones like Apple and Tesla. All of these businesses sell their products directly to the customer.
- Subscription: The subscription business model charges customers a recurring fee to access a product or service, usually monthly or yearly. The subscription model is popular among Software-as-a-Service businesses such as web hosting services. Another variation is to charge a membership fee. This model works with platforms that offer communities or specialized coaching.
Advantages and Disadvantages of E-commerce
Advantages of E-Commerce
- Your online store will be available 24/7, allowing you to earn round the clock
- You can offer a lot of services and products without actually owning an inventory
- E-commerce allows customers and sellers to profit from the comfort of their homes
- Starting an e-commerce business is typically cheaper than starting a physical store
- It is generally easier to scale an e-commerce website than a physical store
Disadvantages of E-Commerce
- Most customers avoid using online platforms due to the lack of a “hands-on†or personal experience
- Dealing with customer issues such as refunds can be a drain on resources and staff
- The e-commerce space is highly competitive regardless of your business model
- Third parties, such as manufacturers and shipping carriers, can influence your business in ways out of your control.
How to Start an E-commerce Business

Create an online store
Here is a list of steps required to create an online store.
1. Find product opportunities
The first step is to know what products you want to sell and the people you will buy them. This step is often the most challenging as it requires you to research the available products, their demand, and the pros and cons of dealing with them.
For instance, you can choose to sell web hosting solutions. In this case, you can own the hosting infrastructure, set up a reseller hosting website, or earn from referring customers to a web host. All three options come with their requirements, pros, and cons, so you should analyze the options available to you and choose the one that aligns with your interest, profit level, and resources. If you are dealing in physical products, you must decide if you will create them yourself or get them from a supplier.
2. Create a business plan
We recommend that you formulate a business plan at this stage. A business plan is a document that serves as a guide for your business. It details how you would launch, market, and grow the business. Sections in the business plan will include market research for your chosen product, the industry, and competition. It will also include how to reach potential customers effectively, your shipping strategy, and how to profit.
3. Set up your online store
Once you have researched the product and developed your business plan, it is time to launch it. The first step here is to choose a business name. Generally speaking, you want a business name that is short, memorable, and easy to spell. In most cases, the business name will also be your domain name. Check this article for pointers on the best domain registrars.
After creating your business name and corresponding domain name, you should make a business logo. While you can pay a professional for this, many free platforms, such as Canva, allow you to create beautiful, unique logos.
Once you’ve done that, it is time to build your online store. We recommend using an e-commerce website builder. Alternatively, you can create a store on an online marketplace like eBay or Amazon. You can also combine both.
4. Launch your business
In launching your business, you need to begin working on how to drive traffic to your online store. This step typically requires you to learn about SEO and other digital marketing strategies.
E-commerce Website Cost
The cost of starting an e-commerce business depends on your web hosting, domain registration, and website theme. However, you can spend as little as $100 yearly for cheap yet reliable website hosting providers and responsible domain registries.
Your starting cost will also depend on your e-commerce business model. For instance, if you use the dropshipping or print-on-demand model, you will need less to start since you don’t have to pay for inventory, raw materials, or labor. You only pay for the goods after the buyer has placed an order. For goods you create yourself or source from manufacturers/suppliers, you will need to pay for inventory, materials, labor, and equipment upfront.
E-commerce Website Builder
A website builder is an ideal choice for anyone starting an e-commerce website. Most website builders offer all the features you need for an online store. When choosing an e-commerce website builder, you should focus on factors such as ease of use, the number of templates they offer, their designs, tech support, and platform policies.
Here are some top website builders that e-commerce stores and companies rely on from around the world
Wix – Best for building small online stores
GoDaddy – Best for Creating a Website Quickly
Shopify – Best for large businesses and larger online stores
Squarespace – Best quality website templates suitable for artists and photographers
See more e-commerce website builders here.
E-commerce Website Development
E-commerce website development refers to developing the backend and front end of your e-commerce website. It refers to all the activities involved in building your brand identity to adding functionality to your e-commerce store. These activities include setting up your home page, support pages, product pages, shopping cart, and order form.
Some of the critical areas to consider in e-commerce website development are:
- User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design
- Proper handling of customers’ sensitive financial information
- Great mobile experience
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Smooth sign-up to checkout flow
E-commerce Management

E-commerce management refers to all practices in managing an online business to achieve its goals successfully. It begins by identifying your e-commerce business goals and achieving them by leveraging business tools, team members, and emerging opportunities.
- Inventory management refers to selecting products, developing web-specific product lines, and creating pricing models.
- Order fulfillment: It ensures that products get from the warehouse to the buyer quickly at a reasonable cost. An e-commerce manager or a management team often carries out this process.
- Customer acquisition: The operations team or e-commerce manager will ensure that the products listed on the website are correctly labeled and comply with the highest possible standards. They will then work with the marketing team to develop a marketing strategy for the products. These strategies may include social media marketing, SEO marketing, affiliate programs, etc.
- Customer service: E-commerce management also includes customer retention. Customer retention begins by optimizing the user experience, using the right marketing campaign, improving customer support, and offering incentives to turn customers into repeat buyers.
E-commerce Marketing

E-commerce marketing (also called e-commerce advertising) refers to all the activities and processes involved in building awareness around an e-commerce brand and its products. E-commerce marketers can use channels such as search engines, social media, and other forms of digital marketing to attract potential customers and encourage them to take the desired action.
While e-commerce marketing builds awareness and action toward your product or service, e-commerce advertising focuses on reaching your target audience to promote your product.
Types of E-commerce Marketing
- Social Media Marketing: Most e-commerce marketing happens on social networks, with most of the advertising happening on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, TikTok, and Youtube. E-commerce marketers can leverage these social media platforms, particularly Instagram and Facebook, by using shoppable content that entices visitors to buy immediately.
- Content Marketing: For e-commerce, content marketing refers to your product page copy, relevant blog posts, product-related videos on Youtube, FAQs, and other forms of content that establish your brand as a reliable business in your niche. You can also submit guest posts for external websites with backlinks pointing to your online store and products.
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM) includes search engine optimization (SEO) and paid advertising. SEO focuses on organically ranking higher in search engine query results, while SEM involves paying to have your business or products appear in top spots on search engine results pages. Under SEM, you have activities such as display campaigns, pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, or product-specific ad campaigns (think Google Shopping).
- Email Marketing: When it comes to e-commerce marketing, email marketing is one of the tested and trusted avenues to try. With segmentation, audience-specific content, and trust building, it can become a gold mine for converting leads into loyal customers. The trick is to build your email list correctly and stay consistent.
- Influencer Marketing: This term refers to working with a social media personality or celebrity with a large following that includes your target audience. Most people trust the influencers they follow on social media. When these influencers recommend your products, their followers will likely visit your online store to make a purchase.
- Affiliate Marketing: According to Hubspot, 81% of brands employ affiliate marketing. This huge demand is because you only have to pay the affiliate marketer when they achieve your desired goal, such as making a sale, generating a lead, or building your email list.
- Local Marketing: This strategy targets potential customers within a specified geographical location. For instance, you can offer discounts and incentives to people who reside in an area where your shipping facilities and warehouse are located.
Challenges of E-commerce

All e-commerce businesses face challenges and difficulties. Here’s a brief overview of some of the top issues.
Cybersecurity
E-commerce sites, whether small or large, have to employ the right cybersecurity policies and tools. These procedures and tools, such as tighter access control and data security software, will create a solid cybersecurity framework to help keep data safe and secure. It will also create a response plan that shows appropriate steps in the case of a cyberattack.
Competition
E-commerce businesses must keep up with the competition in terms of pricing, customer service, and product quality. A small business can overcome the competition by leveraging strong values that other competing brands cannot offer. This approach allows the brand to stand out from other e-commerce businesses and attract new customers for your business.
Order fulfillment
Order fulfillment can be challenging when the orders are more than the business can handle. In such a case, outsourcing order fulfillment and e-commerce shipping can be the best solution. A third-party fulfillment company can ease your workload, increase efficiency and streamline the customer experience.
Customer experience
One advantage brick-and-mortar stores have over e-commerce businesses is that they can offer a personalized shopping experience. Online stores can create this personal experience through pricing and customer segmentation. Doing so requires careful implementation of data analysis and tools such as cookies to properly segment the customers and prove a truly enriching shopping experience.
Quality website traffic and visitor conversion
The goal of any e-commerce website should be to convert visitors to customers. This goal can be challenging due to the complexity involved in each industry. However, one solid tip that works is to ensure the website is mobile responsive, user-friendly, clean, and virus free. Leveraging SEO tools and techniques such as short-tail and long-tail keyword research are vital in this area.
Visibility
In the past, simply setting up a great e-commerce website was enough to attract customers. In this age of increased competition, small businesses struggle with visibility. The solutions to the visibility challenge include keyword research, SEO best practices, and building high-authority links.
Return and Refund Policies
In a perfect world, your customer loves the products you are selling and never wants to return them. In reality, a purchaser can have many reasons to return a product. While no business wants to deal with returned goods, you must have a good return and refund policy, as this could be the difference between success and failure. For your business to thrive, you must make customer satisfaction your priority. Be transparent in your return policy. Make it quick, fast, and easy to understand.
History of E-commerce
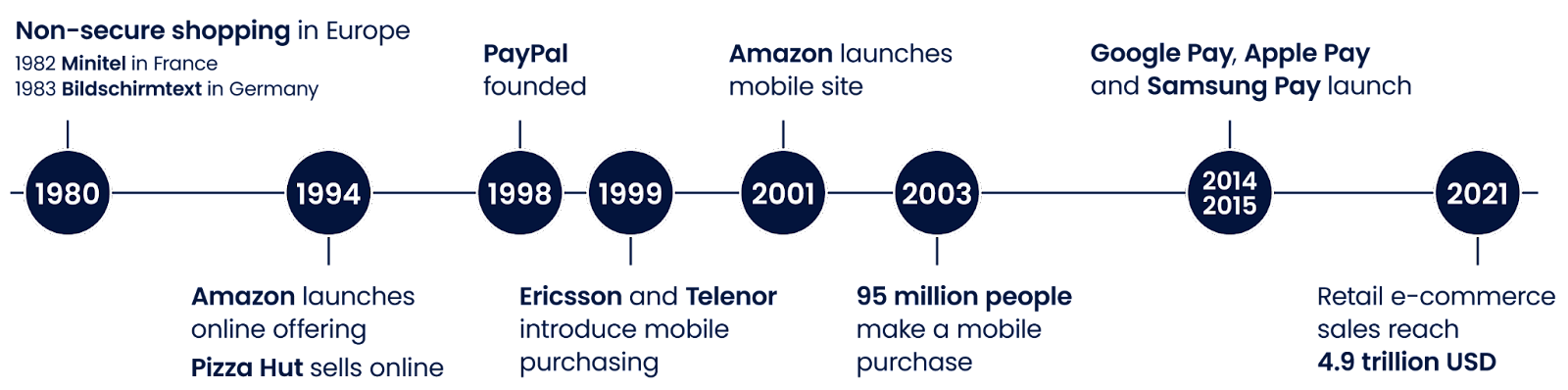
E-commerce might seem like a recent innovation, but it has been ongoing for over half a century.
The first version of e-commerce as we know it started in 1979 when UK entrepreneur Michael Aldrich connected a modified domestic television to a real-time multi-user transaction processing computer via a telephone line. Then in 1992, Charles M. Stack created Book Stacks Unlimited, an online bookstore. The store started as a dial-up bulletin board three years before Amazon joined the online business industry.
The first online transaction happened in 1994, as chronicled by the New York Times. On the 11th of August, 1994, Phil Brandenberger of Philadelphia bought a copy of the compact disk Ten Summoners’ Tales by the rock musician Sting online and paid by sending his Visa credit card number via a secret code for the CD.
Even then, online shopping safety was a concern for many, spurring the development of a security protocol, Secure Socket Layers (SSL). The SSL is an encryption certificate created by Netscape in 1994 that provided a safe means to transmit data over the internet. Web browsers could use an authenticated SSL on a site to determine whether or not users could trust a site.
Presently, the e-commerce space has blown up to become one of the biggest marketplaces in the world, with businesses such as Amazon, Alibaba, and eBay controlling a sizable chunk of the market.
E-commerce Statistics and Trends
Online shopping has steadily grown, with emerging brands competing against global standards. The e-commerce industry has grown in billions from 2017 to 2025
Current projections estimate that e-commerce transactions will rise from $992 billion in 2022 to $2.9 trillion in 2026. And brands are looking to be a part of that growth.
Shopify further projects that most of the competition will happen over social media since that is where most internet users reside. Brands worldwide are leveraging social media to engage, convert, and retain customers out of the projected 4.74 billion social media users worldwide.
E-commerce services and companies
E-commerce services have grown worldwide, with many companies worth billions and even trillions in stock valuation. According to Influencer Marketing Hub, e-commerce accounts for over $5 trillion in annual retail sales globally, accounting for 13% of the total retail industry.
Here are some of the big names in the online retailing industry:
Amazon
Amazon is the king of e-commerce, with an estimated 41% share of the US e-commerce market. It recorded a whopping 2.1 billion visits in January 2022 and is perhaps the most-known online retailer worldwide. The platform launched as an online bookstore in 1994 but now deals in a wide range of products, such as electronics, fashion items, furniture, and toys.
eBay
Apple
Etsy
Walmart
E-commerce Tools
Here is a rundown of businesses in different sectors that leverage e-commerce.
- E-commerce platforms and software include software that enables you to build and manage e-commerce websites. They include popular platforms like Shopify, BigCommerce, Big Cartel, and Squarespace. You can also use a regular website theme and e-commerce plugins for enhanced functionality.
- Content creation tools are tools you use to create, design, and manage content. They include design tools like Canva and content management tools like WordPress.
- Communication and productivity tools are essential for online businesses to manage internal operations and communication. They include Slack, Coda, and Monday.com.
- Sales and logistics tools are essential for inventory and order management. The popular standalone options are Shipwire and Veeqo.
- Marketing is an essential aspect of e-commerce, so it is supposed that only a few marketing tools are dedicated to each aspect of marketing. Examples include Mailchimp and Constant Contact for email marketing and Buffer for social media management.
- Analytics tools allow business owners to measure performance, consumer behavior, and ROI on marketing stories. They include the popular Google Analytics and the less popular Optimizely.
- Customer service is a vital aspect of e-commerce as it affects customer loyalty, which is a crucial determinant of profitability. Some of the e-commerce tools that help with customer service are Acquire and Zendesk.
E-commerce Applications
E-commerce can be applied in many sectors, from wholesale/retail to digital advertising and even auctions. Here is a brief rundown of the most common applications of e-commerce.
- Retail and Wholesale: You can apply e-commerce in many ways. Some examples include business-to-customer and business-to-business models and m-commerce, where customers purchase products via mobile phones.
- Online Marketing: This includes a wide range of aspects, including getting customer data, fixing prices, and building solid brand-customer relationships.
- Finance: Financial institutions such as banks and lending institutions now use e-commerce to add functionality to financial products. Now, customers can carry out a wide range of transactions via electronic channels such as computers and mobile devices.
- Online Booking: Physical businesses such as airlines, hotels, and recreation parks now leverage e-commerce to allow customers to set up reservations, make payments and leave feedback via electronic channels.
- Digital Advertising: Digital advertising is selling an idea to a target audience in the hopes that they would make the steps desired by the advertisers. These ads can come in different forms, such as social media ads, search engine marketing, and pop-up ads.
- Auctions: Online auction platforms allow auctioneers to offer their products to a wide range of audiences, thereby boosting publicity and profit. eBay is one of the world’s most robust online auction platforms.
Benefits of E-commerce over Brick-and-mortar
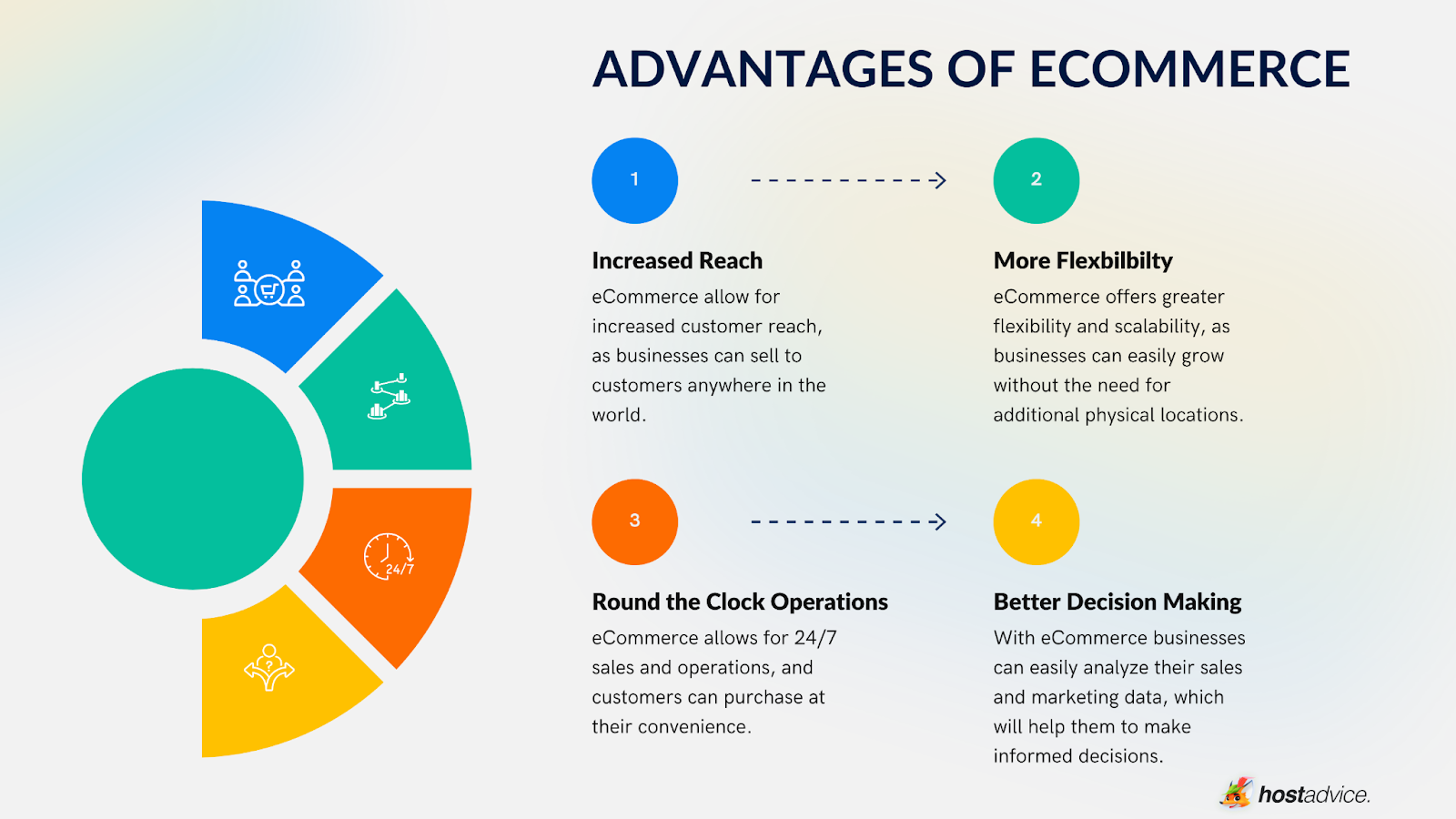
Easy to scale
Unlike brick-and-mortar businesses, expanding an online store is budget-friendly. You don’t need to rent more space, hire more employees or even move to a second location. In most cases, all you need to do is increase the hosting resources allocated to your website. You may need to rebuild your website for massive expansions, but the costs are far less than revamping a physical store.
Increased customer reach
An e-commerce website does not have geographical restrictions like a physical store. This means more people can shop online than at your physical store. This allows you to grow your customer base and grow your business rapidly.
Round-the-clock sales
A brick-and-mortar store typically has opening and closing hours. The store can only mark sales when it is opened, meaning you must always be present or hire a night staff if you want to make sales 24/7. An online store doesn’t have that limitation since it is available around the clock. Furthermore, 24/7 availability requires no extra expense, allowing you to make sales while you sleep at no additional cost.
Conclusion
E-commerce is the use of the internet to make transactions and data transfers. Starting an e-commerce business offers many benefits. However, it also comes with its share of challenges. It can serve as a standalone source of income or an addition to an existing form of income. With the right tools, knowledge, and support, anyone can create a thriving e-commerce business.
Next Steps
- Choose a domain registrar for your business name
- Choose the best website builder for your e-commerce website
- Learn how to boost your website SEO
- Save cost by choosing a cheap yet reliable web hosting provider







